Commonly referred to as androgenetic Alopecia Alopecia or male-design baldness, hair loss in men is a disorder that can seriously impact a man’s quality of life. The usual symptoms are a receding hairline, thinning of the top of the head, or bald spots.
Several causes, such as age, hormone fluctuations, and heredity, can cause hair loss in men. Over 50% of males over 50 are predicted to experience some hair loss. In addition to its clinical manifestations, this illness can have a powerful psychological effect on people.
Understanding reasons hair loss in men
- First, if Alopecia develops, men should recognize the problem and seek suitable hair loss treatment for men.
- Second, understanding the causes and cures of hair loss in men can alleviate the psychological stress associated with hair loss by providing men with knowledge and control over their situation.
- Third, understanding the causes and treatments of hair loss in men can dispel myths and misconceptions, leading to better management of expectations and outcomes. Recognizing the significance of hair loss is the first step towards addressing this common yet profoundly personal issue.
Understanding Hair Loss in Men
Alopecia, often known as hair loss, is the thinning or lack of hair in areas where it typically grows, particularly on the head. This ailment may impact your scalp only or your complete body and may be transient or irreversible.
Losing fifty to one hundred hairs every day is typical. You have over 100,000 hairs on your head, so little loss is invisible. The lost hair usually grows back; however, this is not always the case. Hair loss can occur abruptly or gradually over years and can be temporary or permanent.
Types of Hair Loss in Men
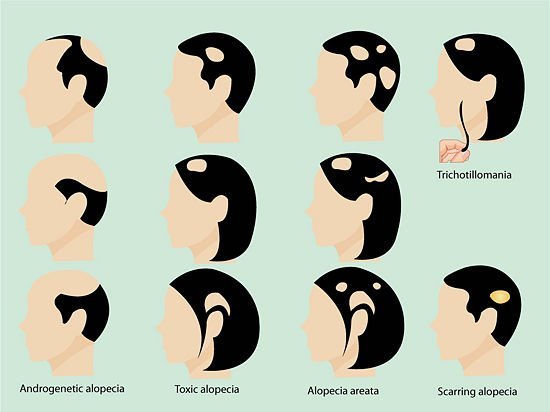
- Androgenetic Alopecia, male-design baldness, is characterized by a receding hairline and removal from the crown and frontal scalp. It is thought to be inherited and is the most prevalent form of hair loss in men.
- Telogen Effluvium is a provisional condition caused by significant body stress, such as surgery, weight loss, or a severe illness. This stress can cause hair to prematurely enter the telogen (resting) phase and fall out.
- Areata Alopecia An autoimmune infection called alopecia areata frequently causes erratic, uneven hair loss. In some instances, alopecia totalis, or total baldness, may result.
- Alopecia scarring, sometimes called Alopeciaicial alopecia, is permanent hair loss that results from inflammation-induced destruction of hair follicles and their replacement by scar tissue.
The characteristics of each type of hair loss in men vary, and different treatment modalities may be needed. People should speak with healthcare professionals to identify the kind of hair loss they are having and the best course of action.
Causes of Hair Loss in Men
- Genetics
- Hormonal Changes
- Lifestyle Factors
- Medical Conditions
Chronic stress can worsen hair loss in men. Manage stress with yoga, meditation, and regular exercise to improve overall well-being and hair health.
Symptoms and Patterns of Hair Loss In Men

Common Symptoms
- Gradual Thinning on the Top of the Head: One of the men’s most common hair loss symptoms is the gradual thinning of hair on the top of the head. This often starts with a slight reduction in hair density, which can be difficult to notice initially. Over time, the thinning becomes more pronounced, leading to a noticeable decrease in hair volume. This symptom is a hallmark of androgenetic AlopeciaAlopecia and typically progresses slowly.
- Receding Hairline: A receding hairline is another typical indicator of hair loss for men. On the forehead, it frequently forms an “M” shape that extends backwards from the temples. Male design-baldness can begin as early as the late teens or early twenties; this pattern is frequently one of the earliest symptoms. Over time, the hairline gradually recedes, which can drastically change one’s appearance.
- Patchy Bald Spots: Patchy bald spots, or alopecia areata, are alopecia hair that fall out in small, round patches. This condition is less common than androgenetic AlopeciaAlopecia but can occur at any age. The bald patches can appear suddenly and may be accompanied by itching or discomfort in the affected areas. While some men may experience just a few patches, others might have more extensive hair loss.
Hair Loss Patterns
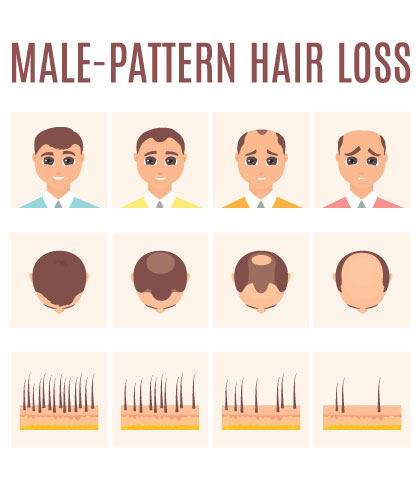
- Male Pattern Baldness (Norwood Scale): Male pattern baldness is categorized using the Norwood scale and usually follows a recognized pattern. On this scale, stage 1 corresponds to little to no hair loss, and stage 7 corresponds to little hair loss, leaving only a rim of hair around the edge of the scalp. The Norwood scale aids in determining the degree of hair loss and developing the best course of action for therapy. Each person’s journey through the phases is unique and impacted by hormonal and genetic variables.
- Diffuse Thinning: Diffuse thinning is characterized by an overall hair thinning across the scalp rather than in localized patches. This type of hair loss can be more challenging to detect initially, as it does not follow the typical patterns of male pattern baldness. Men experiencing diffuse thinning will notice a reduced hair density, making the scalp more visible. Various factors, including stress, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions, can cause this condition.
If know these signs and patterns of hair loss in men, they can seek suitable therapies and effectively manage them. This knowledge can aid in earlier detection and management.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss in Men
Medications
- Overview of FDA-Approved Treatments: Finasteride and minoxidil are the two main FDA-approved treatments for hair loss. Minoxidil is a topical medicine that may be bought over the counter and is administered straight to the scalp. It encourages thicker hair growth, extends the hair cycle’s development phase, and activates hair follicles. The hormone DHT, which is connected to the shrinkage of hair follicles, is prevented from being produced by the oral prescription drug finasteride. Although they must be used consistently to sustain effects, both therapies have demonstrated efficacy in decreasing hair loss and, in some instances, regrowing hair.
Surgical Treatments
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Men with considerable hair loss can access popular and effective hair transplant surgery. Hair follicles from a donor area—typically the back of the head—are extracted and transplanted to balding or thinning areas. The two primary methods are FUE and FUT transplantation . In FUE, individual follicles are extracted, whereas in FUT, a strip of scalp is withdrawn and divided into individual grafts. Both techniques yield natural results, but FUE requires less downtime and less time to recover from.
- Scalp Reduction and Flap Surgery: Scalp reduction involves surgically removing bald scalp areas and stretching the remaining scalp with hair over the bald spot. This method is less common today due to advancements in hair transplant techniques. Flap surgery, another less standard procedure, involves moving a flap of hair-bearing scalp to a bald area. These procedures are more invasive and can have a higher risk of complications than hair transplants.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Low-Level Laser Therapy: Red light wavelengths are used in low-level laser therapy (LLLT), a non-invasive procedure that stimulates hair follicles and encourages growth. It is thought to improve cellular activity in the follicles and raise blood flow to the scalp. Various equipment, such as laser combs, helmets, and hats, can be used to administer LT, which is considered safe and has few negative consequences. Usually, it takes many months of consistent use to observe any discernible effects.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Blood is drawn from the patient, processed to concentrate platelets, and then PRP is injected into the scalp as part of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. Through the promotion of tissue regeneration and angiogenesis in the scalp, this treatment seeks to increase hair thickness and accelerate hair growth.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Smoking can worsen hair loss in men by damaging hair follicles and reducing blood flow to the scalp. Quitting smoking can improve hair health and slow the progression of hair loss.
Preventive Measures for Hair Loss in Men
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment:
Early detection and treatment of hair loss in men can significantly slow its progression and enhance the effectiveness of interventions. Individuals can seek professional advice and start appropriate treatments sooner by recognizing the signs of hair loss early, such as thinning or a receding hairline. Early intervention with medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride can help maintain existing hair and promote regrowth. Early lifestyle adjustments and hair care practices can prevent further damage and preserve hair health.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Hair Care Routine
Keeping your body hydrated is essential for overall health, including the health of your scalp and hair. Drink plenty of water daily to maintain optimal hydration and support hair growth.
Psychological Impact of Hair Loss in Men
Emotional and Social Effects
Seeking Professional Help
Conclusion
Although managing hair loss in men can be challenging, it’s important to keep in mind that support and tools are available. Men experiencing hair loss are advised to consider multiple treatment choices, seek assistance early on, and decide which alternative or treatments best suit their needs.
Hair loss in men can be effectively managed and even reversed using various techniques, including lifestyle modifications, non-surgical therapies, medication, and surgery. Accepting these answers can significantly raise one’s quality of life and self-esteem.
FAQs for Hair Loss in Men
What are the main reasons why guys lose hair?
The following are the leading causes of hair loss in men:
Genetics (also known as inherited hair loss or androgenetic AlopeciaAlopecia).
Changes in hormone levels, such as higher grades of dihydrotestosterone or DHT.
Components of a lifestyle (such as stress, diet, and smoking).
Health problems (such thyroid problems or alopecia areata).
Unfavourable consequences of particular medications.What options are there for treating Hair loss in men?
Men with hair loss may benefit from non-surgical treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), surgical treatments like hair transplant surgery, lifestyle modifications, and home remedies like mild hair care routines and dietary changes.
How long do hair loss treatments take to show results?
Depending on the type of treatment and each patient’s response, the time frame for observing outcomes from hair loss therapies varies. For instance, it may take several months of persistent treatment for drugs like finasteride and minoxidil to show any discernible changes. Yet, it may take several months for the full effects of surgical procedures, such as hair transplant surgery, to manifest.
Do any adverse effects accompany therapies for hair loss?
Finasteride is one medication for hair loss that may have unintended consequences. Before beginning therapy, addressing any potential side outcomes with a healthcare provider is imperative. Risks from surgical treatments include infection and scars, but these are uncommon and can be reduced with appropriate management.
Is it possible to fully reverse hair loss?
The degree to which hair loss can be stopped depends on several variables, such as the underlying reason, the severity of the loss, and the patient’s reaction to therapy. Complete reversal may not always be achievable, even though some therapies can reduce or eliminate hair loss and encourage regrowth. Nonetheless, many people may significantly enhance their appearance and hair density with the right course of treatment.
Does hair loss indicate a more serious medical issue?
Hair loss can periodically be a sign of underlying medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases or thyroid problems. However, the leading causes of hair loss in males are genetic or associated with ageing and hormonal changes. Speaking with a medical expert to rule out any underlying conditions causing your hair loss is necessary.
Do any all-natural treatments for hair loss exist?
Some people consider natural medicines like saw palmetto or essential oils like rosemary or peppermint supplemental hair loss therapies. Although there isn’t much scientific proof to back up these therapies’ efficacy, some people could find them helpful when combined with other comprehensive hair care techniques. Before attempting natural treatments, please consult a healthcare provider to confirm they are safe and appropriate.

