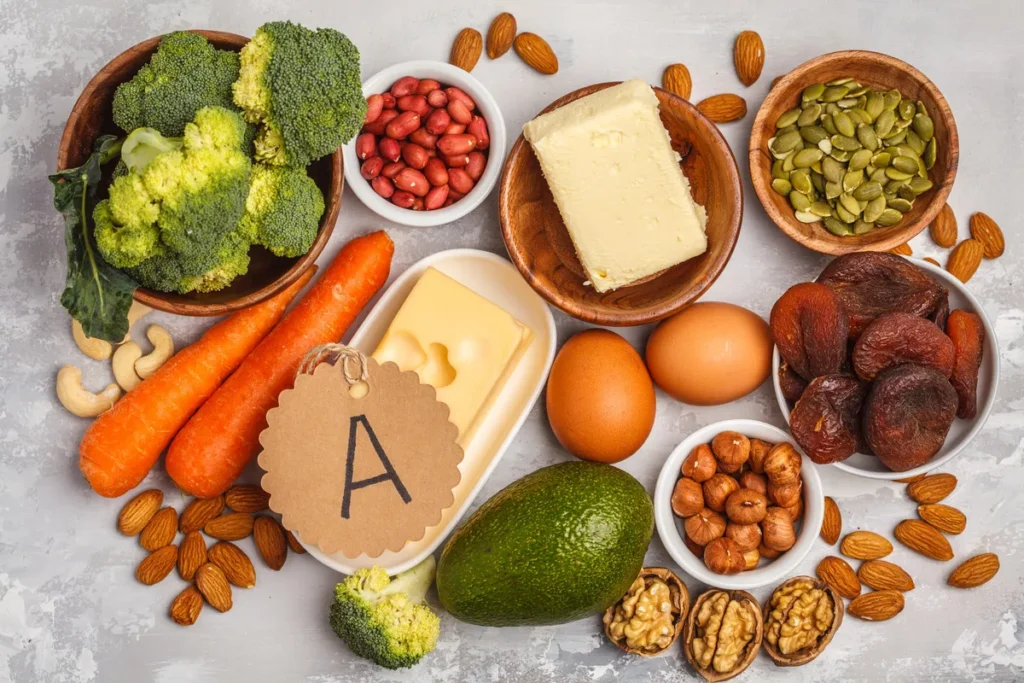
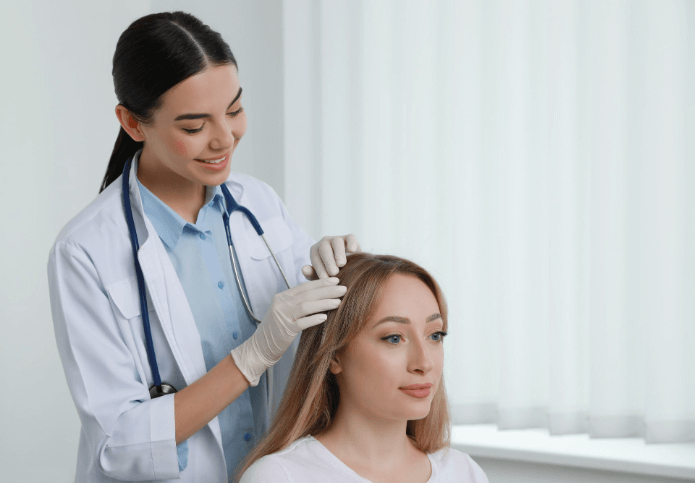
Hair growth supplements for women are one of the best ways to improve the general quality and thickness of hair in women, as well as the health of their hair.
Depending on the circumstances, the condition of the hair is sufficient to confirm the cleanliness of any man or woman and there, or, on the contrary, there.
Thus, the enhanced interest in hair extensions for women is not only a purely local trend but a worldwide one. It is important to take note of this increased demand, as it affirms the desire of women all over the world to have beautiful, healthy-looking, and shiny hair.
Discover the specific vitamins that can accelerate hair growth and explore a range of hair growth supplements for women. These supplements can be a game-changer in your hair journey, helping you achieve vibrant, healthy hair when paired with the right routine and shampoo. Transform your hairstyle and enjoy the benefits of a well-rounded hair care approach today!
Hair Growth Supplements for Men Can Prevent Baldness. Examples of men’s hair growth products include collagen and Omega-3s, which aid in promoting the growth of healthy hair.
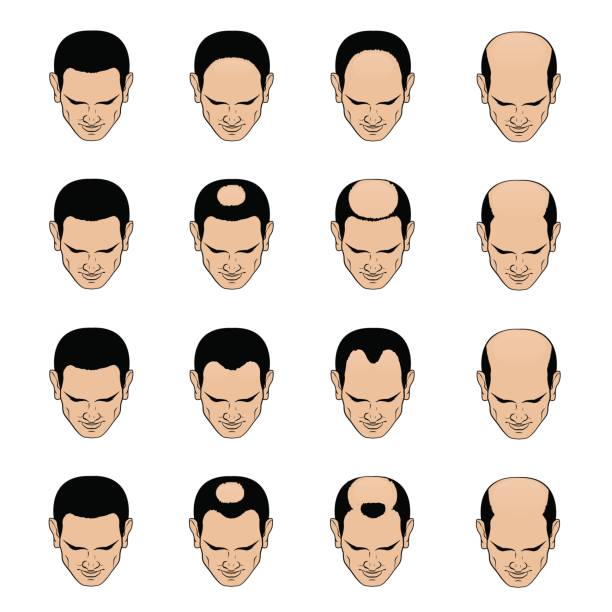
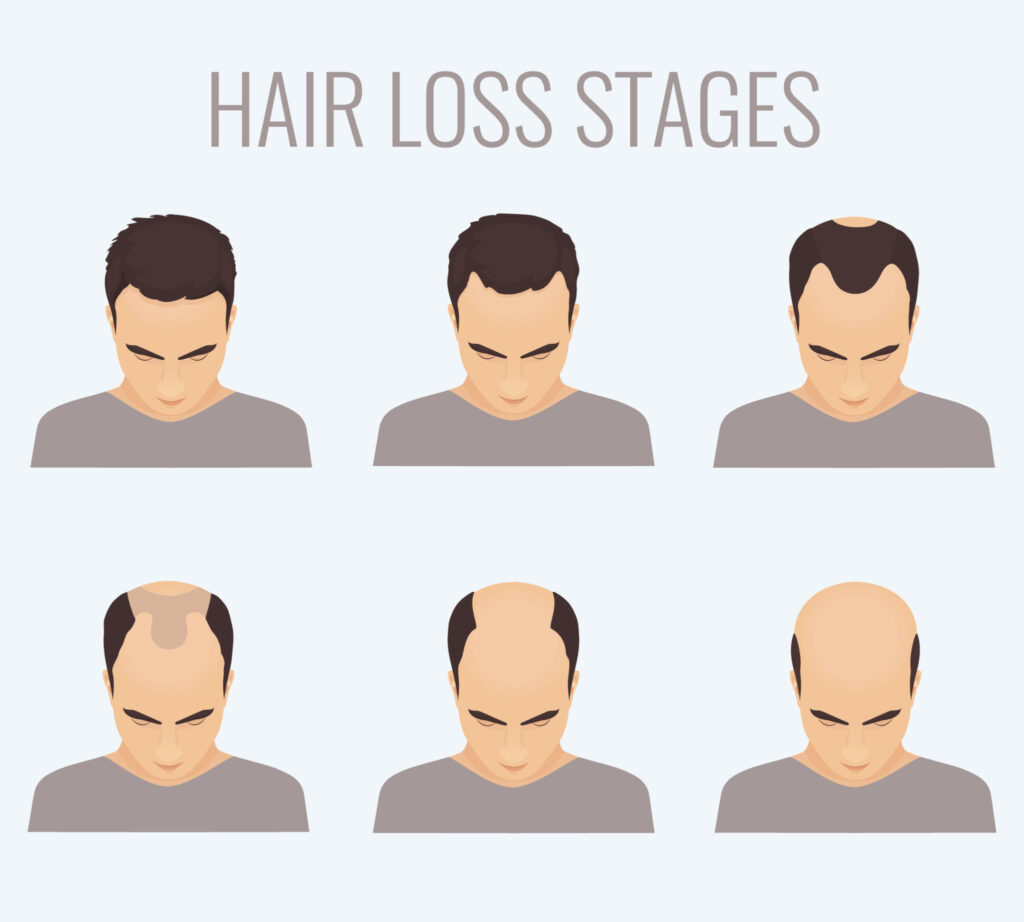
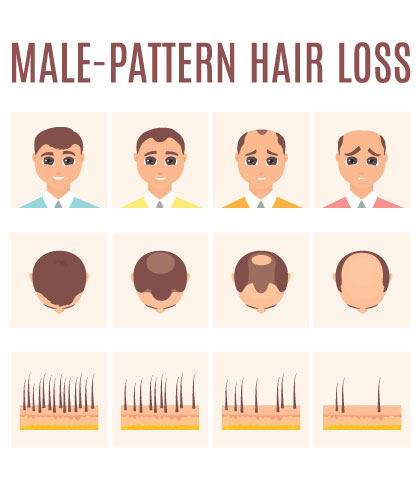
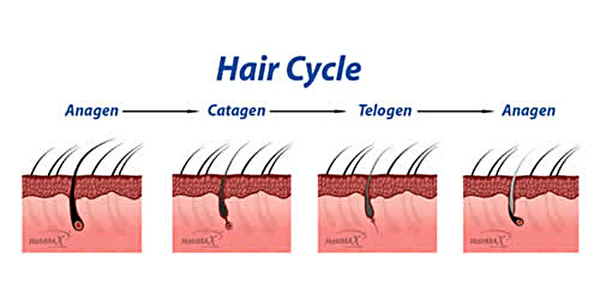
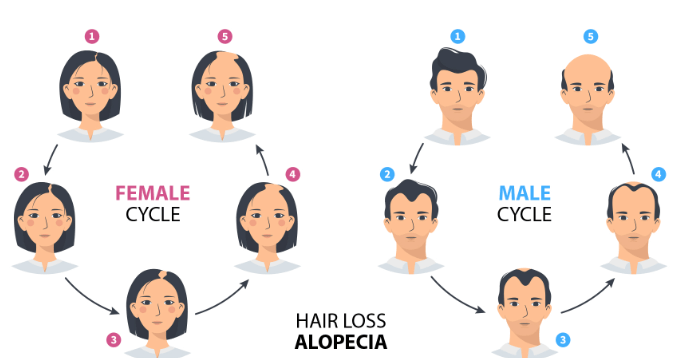
Hair Growth Cycle
Hair growth is an energetic and uniform cycle with three unique phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen. Each phase is vital to hair development and renewal.
1. Anagen phase: The growth phase is known as the anagen stage, where hair follicles produce hair that grows until it completes its life cycle. This phase may last from two up to six years, determining the length of our hair.
2. Catagen Phase: When the anagen phase ends, your hair enters the catagen phase, which takes about two to three weeks. Here, the hair follicle agrees and separates from the dermal papilla, the cells that are meant to produce hair.
3. Telogen Phase: The third and final part of the hair growth cycle is the telogen phase, also known as the resting phase. This phase, lasting approximately three months, is a time of dormancy for the hair follicle. No new hair development occurs during this period, but rather, the existing hair remains in place until another follicle initiates its own growth process.
What influences the growth of your hair?
- Hereditary factors: Your hair’s propensity to grow, density, and tendency to fall are all partly governed by your genes.
- Your diet: A balanced diet is the base of good hair growth. Vitamin and mineral deficits can lead to thinning and actual hair loss.
- Stress: Increased stress levels can lead to telogen effluvium when the hair shifts into the telogen phase
Being aware of these phases and factors will help you understand how hair growth supplements can aid the natural process and promote hair health in general.
Use gentle shampoos and conditioners, and treat scalp conditions like dandruff, as they can hinder hair development.
What Hair Growth Supplements for Women Do
Hair growth supplements for women can boost growth by supplying the body with features typical diets do not provide. They are ready to give adequate vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to care for hair.
Difference Between Supplements and Topical Treatments
| Provider | Supplements | Topical Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Method of Delivery | The essential contrast lies in the delivery method. Supplements are taken inside the body. | At that exact time, topical effects are used directly on the scalp and hair. |
| Systemic vs. Localized Effect | Supplements produce a systemic effect that can help the whole body, including the hair. | On the other hand, topical effects have a localized effect and target a specific area of the scalp or hair. |
| Long-term vs. Short-term Results | Supplements usually need to be taken over some time to reach desired results as they aid ongoing processes in the body. | Topical products may offer quicker results but only produce a long-term impact with ongoing use. |
Offering vitamins to your hair care habit may be an ideal way to boost hair growth and health. Yet, it is essential to choose the right supplement for your needs and check with your doctor before starting any supplement.
Hair growth supplements for women take time. You allow at least three months to see noticeable changes.
Types of Hair Growth Supplements for women

- Vitamins and Minerals
1. Biotin (Vitamin B7):
Significance: Biotin is needed to influence keratin, a protein found in hair, skin, and nails. Biotin helps keep the keratin system, which can push hair healthier.
Uses: It reduces hair thinning, enhances hair texture, and boosts hair growth.
2. Vitamin D:
Significance: Vitamin D generates new hair strands and microscopical spaces through which it sprouts. People without the necessary means have impoverished follicles and may be unable to grow long locks.
Uses: Regulates cycles so strands do not break easily, resulting in more hair volume.
3. Iron:
Significance: This mineral aids in producing haemoglobin, which carries oxygen to all body cells, including those found within our skins, but mostly around root bulbs called “follicles.” Poverty leads to a lack of Iron, causing anaemia; hair loss is experienced widely.
Uses: Iron enhances general health by promoting growth and preventing falls by nourishing the body with sufficient nutrients, especially where one has deficiencies or is sick. Iron also boosts blood circulation, thus supplying oxygenated blood into these areas and ensuring they receive enough oxygen for survival.
4. Zinc:
Significance: Zinc contributes to the growth of hair tissues and the repair and maintenance of oil glands around the follicles. Hair loss or scalp problems could result from lack of poverty when in deficiency.
Uses: It enhances more follicles to grow hair, thus reducing dandruff and improving overall scalp health.
- Herbal Supplements
1. Saw Palmetto:
2. Ginseng:
3. Other Herbs:
- Protein Supplements
1. Keratin:
2. Collagen:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids : The following structures and functions support the scalp to promote hair growth:
1. Fish Oil:
2. Flaxseed Oil:
A lady conscious of the distinct benefits of various hair growth supplements for women may select the ones that best suit her growth problems.
Key Ingredients : Hair Growth Supplements for women

- Biotin
Benefits:
Recommended Dosage:
- Vitamin E
How It Promotes Scalp Health and Hair Growth:
- Iron
Why is it essential for hair loss:
- Zinc
Contribute to Hair Tissue Growth and Repair:
- Collagen
Why it is strong hair and Elasticity:
- Herbal Extracts
List of herbal ingredients that work well:
By investigating these ingredients in hair growth supplements for women, ladies can select items more inclined to help their hair and tackle the reasons behind their hair growth issues.
How to Choose the Right Hair Growth Supplements for Women
Evaluating Your Hair Requirements
- Recognize Particular Issues: Are you battling hair thinning, hair fall, slow growth, or brittle hair?
- Potential Causes: Are you going through hormonal changes, nutrient deficiency, stress or hereditary problems?
- Individual Goals: What would you like to achieve by growing your hair? More volume, better texture or less hair fall?
Reading Labels and Ingredients
- Essential Ingredients: Search for vitamins and minerals like Biotin, Vitamin D, Iron and Zinc.
- Doses: Check that the doses of active fixing are sufficiently high to meet the recommended daily admissions. Avoid items with insanely high doses.
- Other Ingredients: Look for additional herbal extracts like Saw Palmetto, Ginseng, and Rosemary. Avoid unnecessary fillers and synthetic additives.
- Allergen Warning: To avoid poor reactions, know about any potentially allergenic ingredients recorded on the mark.
Quality and Brand Name
- Established Brands: Stick to famous, outstanding brands with great reviews and customer testimonials.
- Certified Products: Search for items third-party associations check for quality and safety (e.g., GMP, NSF).
- Open Information: I prefer brands that give total data about sourcing and manufacturing procedures and carry out clinical studies to help their items.
- Comeback Policy: Can you return the item if the enhancement doesn’t satisfy you? Does the organization provide fantastic client service?
Talk to Your Doctor or Medical Practitioner
- Consult an Expert: Before you start taking any new supplements, especially if you are on medication or have an existing health problem, you must talk to your physician.
- Customized Advice: A doctor can recommend better things to inform your hair requirements and well-being further.
- Follow Progress: Regularly observing your doctor can assist them with monitoring your Improvement and changing the supplement routine if necessary.
- Side Effects: Talk to your expert about any reactions or issues with a supplement to ensure it’s safe and effective.
Using these factors, you can choose Hair Growth Supplements for Women that best meet your needs and help you find healthier, stronger hair. For good hair health, always drink enough water, avoid stress, and eat a well-balanced diet with enough nutrients.
Maintain proper hydration, manage stress, and eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support hair health.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Possible Side Effects
Precautions
Conclusion
Women suffering from hair loss problems would find hair enhancement products extremely helpful. In order to make an informed decision in support of hair health, one must consider a woman’s hair growth cycle, factors affecting it, and supplementary types available on the market. Ingredients such as Biotin, Vitamin E, Iron, Zinc, Collagen, and Herbs promote growth while keeping hair healthy.
When picking out female hair growth pills, one must scrutinize their hair type before buying any supplement. Go for famous names in the industry; it’s ideal; nevertheless, consulting doctors should be prioritized over anything else. This guarantees that you select the most fitting for your head’s well-being. Being aware of probable after-effects or needed preventive measures will assist you in using them safely, thereby increasing their efficacy.
Women should be well-informed when selecting and using hair growth supplements. They should always have healthier, fuller, and more vivid hair and increased self-esteem and well-being. Seek the guidance of a professional when designing your ideal hair care regimen.
FAQs for hair growth supplements for Women
Is there any truth to hair that grows faster than others?
Hair-grow supplements work well on most women, although personal circumstances may cause significant differences.
How fast are hair growth supplements for women effective?
People respond differently to this question based on their unique characteristics and hair supplements used. Within a few weeks of taking them, some women can experience improvements in hair health and growth, while others may wait for several months before anything becomes apparent on their heads.
Instead of using hair growth supplements for women, what alternative natural products can women use?
Various other ways exist for those who want to boost their hair growth naturally and have healthy hair. These include eating a well-balanced diet with nutrients, practising stress management techniques, and ensuring the hair is not subjected to intense treatments or harsh products.
When can generally begin using hair growth supplements for women?
Typically, hair growth supplements for women are deemed suitable.It is essential first to understand how these may affect you based on your health and other drugs you might be taking. Before using any new supplement, pregnant moms, nursing mothers, kids, and seniors should seek advice from their physicians.
Do hair growth supplements make hair grow on your chin or in other funny places?
Although rare, some supplements that contain hormonal ingredients can do this, so it is essential to read the labels and ingredients carefully and be mindful of any side effects. Stop the supplement and consult your doctor if you suddenly start growing hair in unusual places.
Are there any dietaries that can affect hair growth supplements for women?
Generally, hair growth supplements for women are ok to take with most diets, although a healthy, balanced, and nutritious diet is needed for optimal results. Some supplements may contain allergens or affect particular foods, so if you have any dietary restrictions, always read the label carefully and consult your doctor.