Ever wonder if there’s a real, proven way to tackle hair loss?
You’re not alone — hair loss is a major concern for many, and the search for an effective solution can feel never-ending.
That’s where Minoxidil 2% comes in. This isn’t some overnight miracle, but if you’re looking for a product that’s backed by science and trusted by users, Minoxidil 2% could be worth a try. It’s a milder concentration of Minoxidil, designed for those who want effective hair regrowth without the extra strength of higher concentrations.
Minoxidil 2% is a popular over-the-counter treatment for hair loss and thinning, specifically designed for women. Known for its effectiveness in stimulating hair growth, it’s a trusted solution for those experiencing early-stage hair loss or seeking a approach to gentlerrevitalize thinning hair. Unlike the stronger 5% formula, Minoxidil 2% offers a milder, less intense treatment, making it ideal for sensitive scalps or first-time users.
Ready to dive deeper? We’re going to cover everything you need to know about Minoxidil 2% — how it works, what kind of results you can expect, and tips on getting the best outcome from your treatment.
Let’s get started!
What is Minoxidil 2%?
Minoxidil 2% is a topical treatment specifically formulated to address hair loss and thinning hair. It’s essentially a lower-strength version of the more commonly known Minoxidil 5%, making it a great choice for those who need a gentler approach or have sensitive skin.
Unlike some hair loss treatments that promise results without evidence, Minoxidil 2% is backed by science and recommended by dermatologists worldwide. It’s designed for people experiencing mild-to-moderate hair thinning, particularly those who want to take action early before hair loss becomes more severe.
Why Choose Minoxidil 2%?

Minoxidil 2% is ideal if you’re dealing with early signs of hair loss. The lower strength is perfect if your scalp is on the sensitive side or you’re just starting out with Minoxidil.
- It’s a reliable first step for individuals new to hair loss treatments.
- Suitable for both men and women, especially those with a sensitive scalp.
- Offers a gradual and less aggressive approach to hair regrowth compared to higher concentrations.
Minoxidil 2% is available in both liquid and foam forms. If you experience irritation from the liquid, consider switching to the foam version, which may be gentler on sensitive scalps.
In simple terms, Minoxidil 2% works by stimulating hair follicles and improving blood flow to the scalp, which helps kickstart the hair growth process and reduce overall shedding.
Who Should Avoid Minoxidil 2%?
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Minoxidil is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Consult a healthcare provider for safer alternatives.
- People with Scalp Conditions: If you have scalp infections, psoriasis, or severe irritation, it’s best to address these conditions before starting Minoxidil.
- Children and Adolescents: Minoxidil is not typically recommended for anyone under 18 years of age unless specifically advised by a doctor.
This overview clarifies the ideal candidates for Minoxidil 2%, helping you decide if it’s the right choice for your hair care needs.
How Minoxidil 2% Works
Think of Minoxidil 2% as a targeted boost for your hair follicles. When applied directly to the scalp, Minoxidil dilates blood vessels, enhancing blood circulation in the treated area. This increased blood flow delivers more oxygen and essential nutrients directly to the hair roots, which is crucial for promoting healthy hair growth.
Key Mechanisms of Minoxidil 2%:
Minoxidil 2% creates an optimal environment for hair growth by nourishing the scalp and reactivating the follicles. Although it’s not an overnight solution, consistent use can lead to noticeable improvements in hair thickness and overall scalp health over time.
Focus on applying the solution directly to the areas of the scalp where hair thinning or loss is most noticeable. Avoid applying it to the hair itself.
How Fast Will You See Results with Minoxidil 2%?
Let’s get real: Minoxidil 2% isn’t a magic wand, but it does work — if you give it time. Typically, you can expect to see noticeable results anywhere from 3 to 6 months after starting treatment. Hair growth takes time, and patience is key here.
What to Expect:
- First few weeks: You might notice an increase in hair shedding. This is normal and means the treatment is pushing out weaker hair to make room for stronger growth.
- 3 months in: Some users start seeing less shedding and a slight thickening of existing hair.
- 6 months and beyond: Consistent use often leads to visible improvements in hair density, with new hair growth becoming more noticeable.
Quick tips to get faster results:
- Apply Minoxidil 2% daily: Consistency is everything. Skipping applications can slow down your progress.
- Maintain a clean scalp: Keeping your scalp free of oil and product buildup helps Minoxidil absorb better.
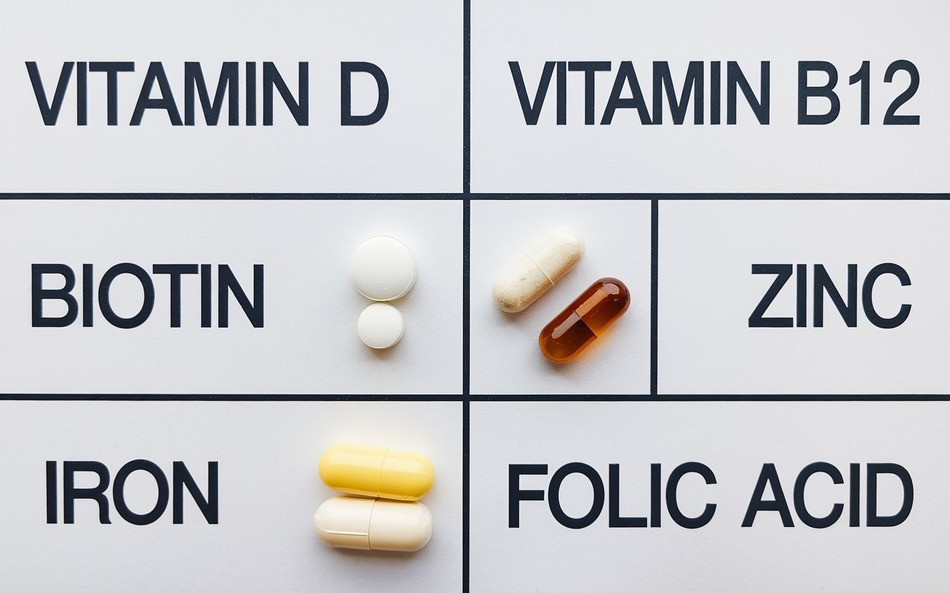
- Boost your diet: A nutrient-rich diet supports hair health. Focus on foods high in vitamins like Biotin, Zinc, and Iron.
It’s a gradual process, but sticking with Minoxidil 2% and following these tips can help you get the best results. Remember, hair growth isn’t instant — but the effort pays off in the end.
Give Minoxidil 2% at least 4 hours to fully absorb into your scalp before washing your hair. Washing too soon can rinse away the solution and reduce its benefits.
Side Effects
Yes, there are potential side effects with Minoxidil 2%, but the good news is that they’re usually mild and temporary. Most users experience little to no issues, but it’s still important to know what could happen.
Common side effects you might notice:
When to see a doctor:
If any side effects seem severe or don’t go away after a few weeks, it’s best to consult a dermatologist. They can help you determine if you need to adjust your treatment or try an alternative.
Remember, most users handle Minoxidil 2% just fine. Side effects are generally mild and temporary, but it’s good to be aware so you know what to expect.
Do not apply Minoxidil 2% to irritated, sunburned, or damaged scalp skin. It can increase the risk of irritation or absorption issues.
How to Apply Minoxidil 2% for Maximum Results
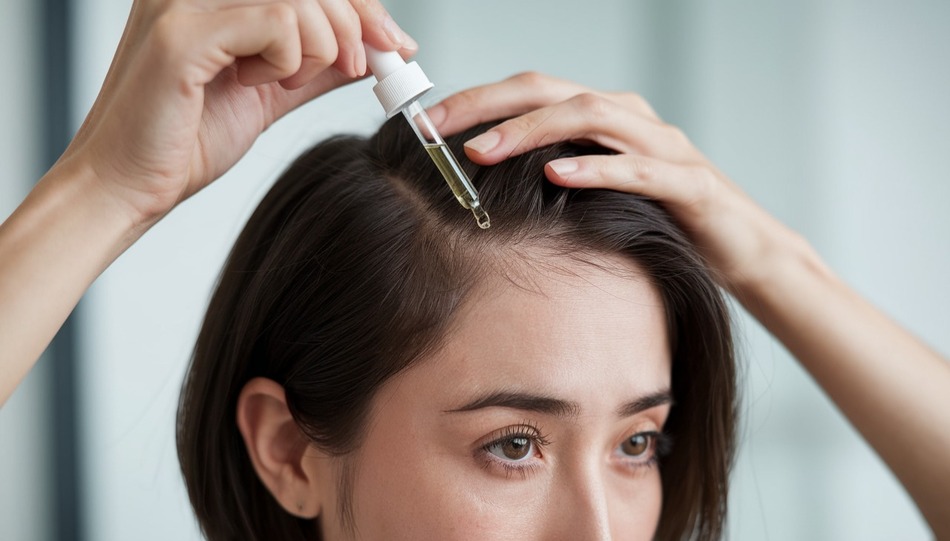

Applying Minoxidil 2% is straight forward, but if you want to see the best possible results, you’ll need to follow a few key steps.
Here’s how to apply it like a pro:
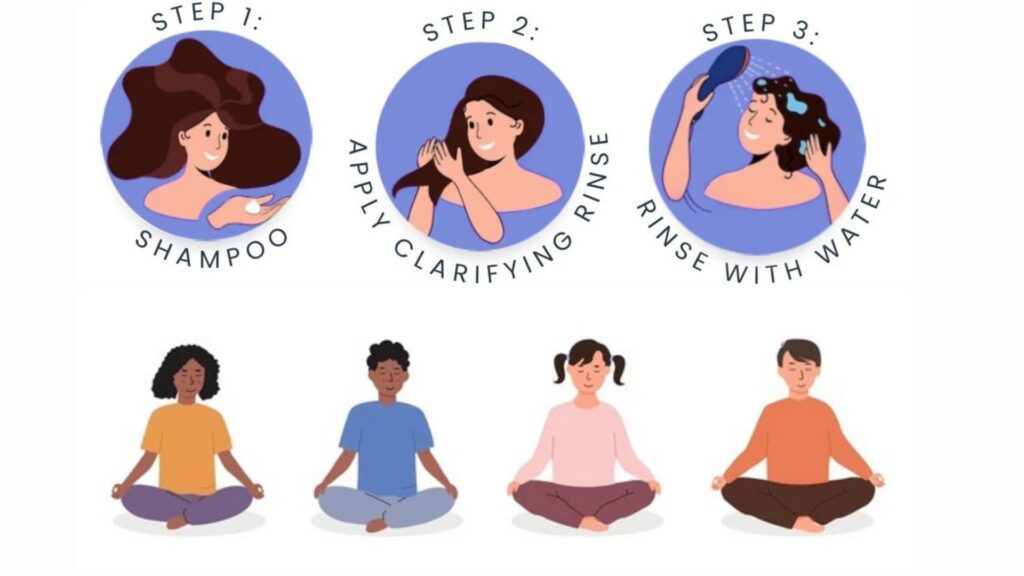
Make sure your scalp is free from oil, sweat, and any leftover hair products. A clean slate helps the Minoxidil absorb better and work more effectively.
Stick to the standard dosage of 1ml per application. Using more won’t speed up results and might just increase the risk of irritation.
After applying the Minoxidil, use your fingertips to massage it into your scalp. This helps the solution penetrate deeper and stimulates blood flow, giving your follicles an extra boost.
Apply Minoxidil 2% twice a day — once in the morning and once before bed. Consistency is key here. If you skip applications, you could slow down your progress.
Pro tips for better results:
- Let it dry completely before styling your hair or going to bed. This prevents the product from rubbing off and ensures maximum absorption.
- Avoid washing your hair immediately after applying Minoxidil. Give it at least 4 hours to fully absorb.
- Consider using a dropper for precise application, especially if you have longer hair.
Consistency and patience are the names of the game. Stick with it, follow the routine, and you’ll give yourself the best chance of seeing thicker, healthier hair.
Wait at least an hour before using a hairdryer, flat iron, or other heated styling tools. Heat can affect the absorption of Minoxidil and may reduce its effectiveness.
Minoxidil 2% vs. Minoxidil 5%: Which One to Choose?
If you’re unsure whether the stronger 5% solution is the better option, let’s break it down to help you decide.
Here’s a table to compare Minoxidil 2% and Minoxidil 5%:
| Feature | Minoxidil 2% | Minoxidil 5% |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Lower strength, 2% concentration | Higher strength, 5% concentration |
| Best for | Beginners, sensitive skin | Experienced users, faster results |
| Expected Results | Gradual hair growth | Faster and more noticeable growth |
| Side Effects | Lower risk of irritation | Higher risk of dryness, redness |
| Recommended Users | Women, cautious users | Men, those seeking faster results |
| Application Frequency | Twice daily (standard) | Twice daily (recommended) |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
If you are taking other medications or have underlying health conditions, check with your doctor before starting Minoxidil 2% to ensure there are no potential interactions.
Conclusion
Minoxidil 2% is a proven, effective treatment for mild-to-moderate hair thinning, offering a gentler approach for those new to hair regrowth solutions or with sensitive scalps. While results take time, with consistent use and patience, many users experience noticeable improvements in hair density and thickness within a few months.
By boosting scalp circulation, stimulating dormant hair follicles, and prolonging the hair growth phase, Minoxidil 2% creates a better environment for healthy hair to grow. Though side effects are generally mild, it’s important to stay consistent with your routine and consult a dermatologist if you experience any issues.
If you’re looking for a reliable and scientifically-backed option for addressing hair loss, Minoxidil 2% could be the gentle, effective solution you’ve been searching for. Stay patient, stay consistent, and you may soon see the positive results of your effort.
FAQs
How long does it take to see results with Minoxidil 2%?
Results vary from person to person, but typically, it can take around 2 to 4 months of consistent use before noticing visible improvements in hair thickness and growth. Full results may take up to 6 months or longer.
Can both men and women use 2% minoxidil?
Yes, Minoxidil 2% is suitable for use by both men and women. However, the 5% solution is typically recommended for men with more advanced hair loss.
Can I use Minoxidil 2% with other hair care products?
Yes, you can use Minoxidil 2% alongside other hair care products. However, avoid mixing it with other treatments unless directed by your doctor. Let the Minoxidil dry before applying any other products to the scalp.
Can I use Minoxidil 2% if I have sensitive skin?
If you have sensitive skin, consult a healthcare provider before using Minoxidil 2%. Some users may experience mild irritation, but this can often be managed by adjusting usage or switching to a lower strength.
Is it safe for women to use 2% minoxidil during pregnancy or lactation?
Minoxidil 2%’s safety during pregnancy and lactation has not been thoroughly studied, therefore women who are pregnant or nursing should speak with their doctor before using it.
Can Minoxidil 2% cause hair shedding?
Yes, some users may experience an initial shedding phase when starting Minoxidil 2%. This is usually temporary and a sign that the treatment works as it stimulates new hair growth.
Can Minoxidil 2% be used on other areas of the body?
Minoxidil 2% is specifically formulated for use on the scalp. It is not recommended for use in other areas of the body without guidance from a healthcare professional.