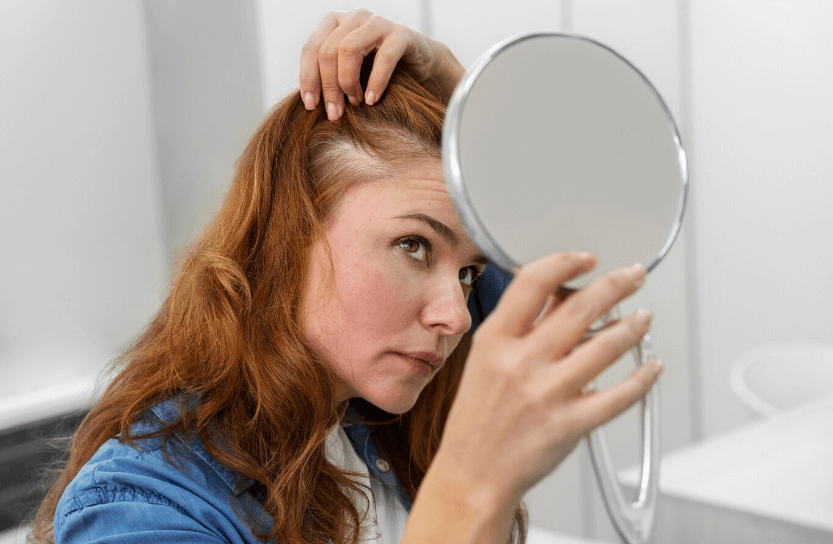
Understanding the role of Dihydrotestosterone, or DHT, in hair loss is crucial. This androgen hormone, a byproduct of testosterone, is a key player in the hair loss process. By gaining knowledge about DHT, you can take control of your hair health and potentially restore your naturally thick, abundant hair.
Delving into the world of DHT for hair and learning how to navigate it is empowering. Understanding the facts about hair loss not only gives you confidence but also equips you with the power to make informed decisions about your hair health.
Knowing the underlying causes of hair loss, such as DHT, is an effective weapon in the fight against it. Hair follicles shrink because the hormone DHT, which is made from testosterone, binds to them, resulting in hair loss. Armed with this knowledge, you may recognize and deal with the problem and other possible factors, including ageing, stress, and heredity.
However, optimism remains! You should be aware that there are treatments like head massages, which improve blood and nutrient supply to the follicles and can stop or even reverse hair loss.
The benefits of massage your head for hair growth include increased blood circulation, which may help hair follicles receive vital nutrients that could promote growth. Moreover, it can aid in muscular relaxation on the scalp, enhancing general scalp health.
What is DHT?
DHT stands for Dihydrotestosterone. It’s a hormone that’s made from another hormone called testosterone. Think of testosterone as dough and DHT for hair as the cookie made from that dough. Our bodies have a special recipe to turn the dough into cookies, and that recipe is an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase.
Here’s how it works:
- Your body has testosterone, which is the main ingredient.
- The enzyme 5-alpha reductase mixes with the testosterone.
- This mix makes DHT.
Dihydrotestosterone is super important because it helps us grow big and strong when we’re young. But sometimes, too much DHT in our scalp can make our hair stop growing and even fall out. That’s why understanding DHT for hair is like learning the secret recipe that can help us keep our hair healthy and whole!
DHT in contrast to testosterone
| Characteristic | Testosterone | Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Parent hormone converted to DHT by 5-alpha reductase enzyme. | Derived from testosterone through the action of 5-alpha reductase. |
| Potency | Less potent compared to DHT. | More potent androgen than testosterone. |
| Androgenic Effects | Promotes development of male sexual characteristics. | More potent in promoting male characteristics like facial hair growth and voice deepening. |
| Role in Health | Essential for overall health in both men and women. | Critical for male sexual development and libido regulation. |
| Hair Growth | Plays a role in body and facial hair growth. | Implicated in male pattern baldness when present in excess in the scalp. |
| Affinity for Receptors | Binds to androgen receptors in various tissues. | Has a higher affinity for androgen receptors, particularly in the prostate and hair follicles. |
How DHT for hair Side Effects
DHT for hair blockers, commonly used to treat conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness, can have several side effects. Here are some of the common ones:
Why some people’s hair is more affected by DHT

Some people are more affected by DHT for hair due to genetic isle breakdown:
- Genetic Sensitivity: Some people have hair follicles that are more sensitive to DHT. This sensitivity is inherited, which means it’s passed down in families.
- Receptor Sites: Hair follicles have places where hormones like DHT can attach. DHT for hair makes people with more of these sites on their follicles more likely to experience hair thinning.
- Androgen Receptors: The strength of androgen receptors in hair follicles also plays a role. More muscular receptors can grab onto DHT more tightly, leading to more hair loss.
- Variations in the 5-AR Enzyme: The enzyme that helps make DHT from testosterone can vary in activity from person to person. More active enzymes mean more DHT and potentially more hair loss.
If hair loss runs in your family and you’re noticing thinning, DHT might be a culprit. It’s akin to a family recipe for a less-than-desirable outcome. Recognizing this connection can guide you and your doctor toward effective strategies to maintain hair health and possibly mitigate the impact of DHT.
How to tell if hair loss is because of DHT
Determining if hair loss is due to DHT involves looking for specific patterns and signs of androgenetic alopecia, commonly influenced by DHT for hair.
If you suspect that DHT for hair is the cause of your hair loss, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. In addition to discussing possible treatments, such as DHT blockers or other medications to manage hair loss, they can offer a diagnosis. other disorders can also cause hair loss, so getting a professional evaluation is essential.
Regular scalp massages can enhance blood circulation to the scalp, which may aid in hair development. Try to get a couple of light massages each week. Massages can improve blood circulation to the scalp, which may promote hair growth. Aim for gentle massages a few times a week.
Ways to treat loss from DHT for hair

Treatment options for DHT-induced hair loss are numerous and can help control the problem. The following are a few of the often-advised treatments:
Although these treatments have the potential to be efficacious, individual outcomes may differ. Before beginning any new hair loss treatment, speaking with a healthcare provider is usually advisable because some therapies could have adverse consequences. They can help you compare the benefits and drawbacks of various treatments to determine which is best for you.
Lifestyle changes and DHT blockers can help manage hair loss.

Your lifestyle choices can indeed impact DHT levels in your body. Here are some ways you can influence these levels:
Remember, while these lifestyle changes can influence DHT levels, the impact may vary from person to person. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
For most hair loss treatments to be effective, constant application over time is required. Have patience and heed the advice of your physician.
Natural ways to block DHT for hair
Here are some natural approaches to inhibit DHT for hair that are validated by scientific research:
It’s important to note that while these natural remedies may help, their effectiveness can vary from person to person. Before trying new treatments, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare expert, especially if you’re sharing significant hair loss. They can guide you on the most appropriate treatment options for your condition.
The best hair loss treatments for women
When it comes to hair loss medicines for women, it’s essential to consider the unique hormonal and biological factors affecting female hair health. Here are some of the best treatment options tailored for women:
- Minoxidil: Available over-the-counter in a 2% or 5% solution or foam, this is the only FDA-approved treatment for female pattern hair loss. Applying it straight to the scalp stimulates hair growth.
- Spironolactone: An androgen blocker that is prescribed medication. It can be very beneficial for women who have hair loss due to hormonal imbalances.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Red light is applied to the scalp using devices like laser combs and helmets, which can be used at home to promote hair ripening.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of intense hair loss, women may consider follicular unit extraction or follicular unit transplant (FUE or FUT), which involves transplanting healthy hair follicles to thinning areas.
- Nutritional Supplements: Deficits in specific vitamins and minerals can cause hair loss. If there is a deficiency, supplements such as zinc, iron, and biotin can help restore the hair’s health.
- Hormone treatment: Hormone replacement treatment is a possible option for women who are undergoing hair loss as a result of menopause or other hormonal changes.
- Topical Treatments: Besides minoxidil, topical medications such as prostaglandin analogues and ketoconazole may aid hair development.
- Dermatological Treatments: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy stimulates hair growth by injecting growth factors from the patient’s blood into the scalp.
- Women should consult a healthcare provider for hair loss diagnosis and treatment options tailored to their health, hair loss extent, and preferences. Individualized care ensures optimal results, as effectiveness varies among individuals.
Not every patient responds to every treatment. Rather than achieving full regeneration, the objective can be to preserve or reduce the amount of hair loss.
DHT blockers can help

Yes, DHT blockers can be quite effective in helping with hair loss caused by DHT for hair. They work by inhibiting the action of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. These DHT blockers lower DHT levels, which can sometimes reverse the hair loss patterns linked to androgenetic alopecia, also referred to as male or female baldness.
Finasteride and Dutasteride are two successful DHT for hair blockers; many users report a noticeable halt to their hair loss and, in certain situations, even considerable regrowth. It’s crucial to remember that every person will experience different outcomes, and not everyone reacts similarly to DHT blockers.
Before beginning any new hair loss treatment, it is essential to speak with a healthcare specialist to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the possible side effects of the treatments.
In summary, while DHT blockers can be a valuable part of a hair loss treatment plan, they should be used under medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Speak with a Medical Professional: Be sure to speak with a physician or dermatologist before beginning any new medication, including DHT blockers. They can assist in determining whether DHT blockers are suitable for your particular health issue.
Conclusion
Comprehending the role of DHT for hair in hair loss is essential for effective management and treatment. DHT, a derivative of testosterone, influences hair growth by attaching to androgen receptors in hair follicles. The enzyme 5-alpha reductase facilitates the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
Genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and hormonal imbalances can all impact DHT levels and contribute to hair loss. By understanding how Dihydrotestosterone functions in the body, individuals can explore various treatment options, including DHT blockers, lifestyle modifications, and natural remedies, to address hair loss concerns effectively—embracing a holistic approach that considers both.
FAQs
-
What is DHT for hair, and how does it contribute to hair loss?
DHT, or dihydrotestosterone, is a hormone derived from testosterone. In some individuals, DHT for hair can bind to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually leading to hair loss.
-
How does DHT affect hair growth?
DHT for hair binds to hair follicles, shortening their growth phase and eventually leading to hair miniaturization, resulting in thinner and shorter hair strands.
-
What factors influence DHT levels in the body?
Genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, ageing, and lifestyle factors such as diet and stress can all influence DHT levels.
-
Are there effective treatments for DHT-induced hair loss?
Treatments such as DHT blockers, topical solutions, oral medications, and hair transplant surgery can help manage DHT-induced hair loss.
-
What are the potential side effects of DHT-blocking treatments?
Side effects may include sexual dysfunction, decreased libido, and scalp irritation, but they vary depending on the treatment method and individual response.
-
Does DHT for hair always cause hair loss, or are there other factors to consider?
While both male and female pattern baldness are frequently caused by DHT for hair, hair loss can also result from other reasons like heredity, illnesses, drugs, and dietary deficiencies.

