Losing confidence, identity, and happiness due to hair loss is like losing a significant and worthwhile aspect of ourselves. But there’s hope with modern hair restoration techniques: FUE and FUT are two surgical techniques of hair transplantation.
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) are two of the most effective strategies in the battle against baldness. This guide empowers you to learn about and contrast these techniques, enabling you to make an informed decision and rebuild your confidence.
Dealing with balding is not easy, as it can significantly impact one’s self-perception. However, there’s a silver lining. Hair transplants, including FUE and FUT, offer a reliable solution to what you’re missing.
Just as important, it is essential to learn these differences. It is not only about hair growth; it is about the most efficient option for you. This guide provides a specification for both techniques to determine which is most suitable for your needs.
So, let me tell you about FUE and FUT hair transplants and help you choose the option that suits you.
What is a Hair Transplant?
Choosing the Right Technique:
Brief History:
Choosing the proper technique is a big decision, and it’s all about what works best for you and your hair goals. A chat with a hair transplant specialist can help you figure out the best path forward.
Types of hair transplant procedures
Hair transplant procedures stimulate hair growth in areas of the scalp undergoing thinning or hair loss. Several methods exist for transferring hair follicles to these balding areas. Here are the main types of hair transplant techniques:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): This treatment involves taking a strip of skin, including hair follicles, from the donor area (often the back of the head) and transplanting it to the balding area. Before being implanted, the strip is first separated into individual follicular units under a microscope.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): In FUE, individual hair follicles are directly taken from the donor area and transplanted into the balding areas using a tiny punch instrument. Compared to FUT, this procedure is less invasive and doesn’t create a linear scar.
- Direct Hair Implantation (DHI): DHI Hair Transplant (Direct Hair Implantation), a variation on the FUE procedure that uses a specialized tool to remove and implant hair follicles directly, allows for more accurate implantation.
- Grafting: Grafting refers to all types of hair transplantation, including FUT and FUE.
- Scalp Reduction: Scalp reduction involves surgically removing sections of the bare scalp and stretching the hair-covered areas toward each other to reduce the bald area.
- Flap Surgery: During this treatment, a healthy scalp section with healthy hair development is transplanted to a bald spot. This allows for the transplantation of several follicles in a single session.
- Tissue Expansion: Using this technique, a tissue expander is positioned beneath a hair-bearing region adjacent to a bald spot. Over time, more hair-bearing tissue grows under the expander, and this tissue is placed over the balding area.
Understanding FUE and FUT
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
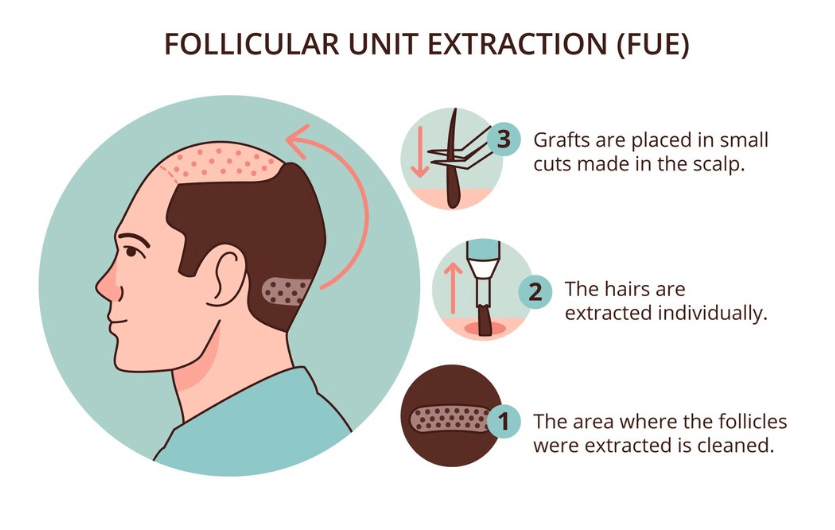
Definition and Explanation of FUE
A sophisticated Hair Transplant procedure called Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) involves transferring individual hair strands from a donor location, often the back or sides of the head, to thinning or balding areas. Older transplant techniques leave linear scars, but this treatment leaves little to no scarring.
Procedure Details: How FUE is Performed
- Preparation: The donor and recipient areas are trimmed and sterilized.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to minimize discomfort.
- Extraction: A technical micro-punch tool carefully removes Unique hair follicles from the donor area.
- Incisions: Tiny, precise incisions are made in the recipient area where the follicles will be placed.
- Transplantation: The extracted follicles are implanted into the incisions, ensuring proper angle and direction for a natural look.
- Post-Procedure Care: The treated areas are cleaned and bandaged, and instructions for aftercare are provided.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FUE
Advantages
- Minimal Scarring: The small, circular scars from FUE are barely noticeable and heal quickly, unlike the linear scar from the FUT method.
- Quick Recovery Time: Most patients can continue normal activities within a few days. The method’s minimally invasive approach minimizes discomfort and downtime.
- Natural-Looking Results: FUE provides a more natural hairline and overall appearance by transplanting individual follicles. The particular arrangement of each follicle ensures a seamless blend with existing hair.
Disadvantages
- Longer Procedure Time: FUE can be time-consuming, especially for more extensive treatment areas, because each follicle is extracted and transplanted individually.
- Higher Cost: FUE is typically more costly because it requires more care and time than FUT. The need for superior technology and knowledge also drives up the price.
- Higher Cost: FUE is typically more costly because it requires more care and time than FUT. The need for superior technology and knowledge also drives up the price.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)
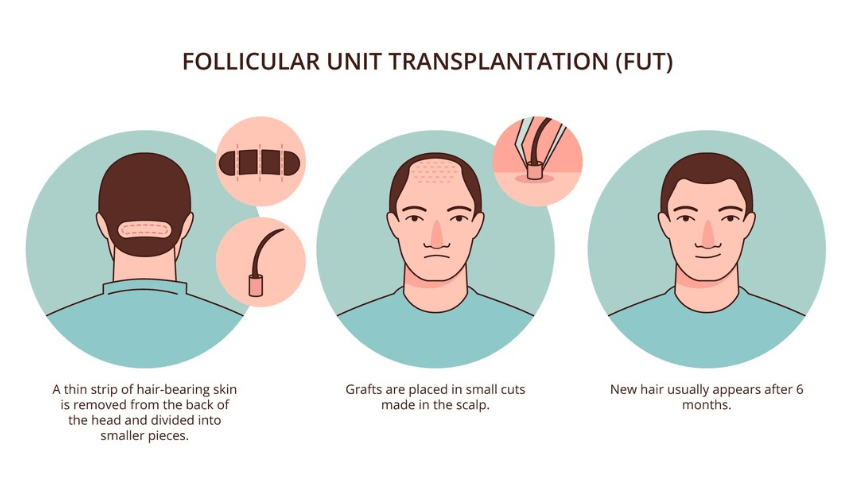
Definition and Explanation of FUT
Strip harvesting, commonly referred to as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), is a conventional hair transplant procedure in which a strip of scalp containing hair follicles is taken from the donor area, usually the back of the head. The strip is then separated into individual follicular units and applied to the balding or thinning areas.
Procedure Details: How FUT is Performed
- Preparation: The donor and recipient areas are prepared and sterilized.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Strip Removal: A strip of the scalp is surgically removed from the donor area. The area is then sutured closed, leaving a linear scar.
- Dissection: The strip is meticulously dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units.
- Incisions: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area where the follicular units will be placed.
- Transplantation: The dissected follicular units are implanted into the incisions, ensuring proper placement for a natural look.
- Post-Procedure Care: The treated areas are cleaned and bandaged, with aftercare instructions provided to the patient.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FUT
Advantages
- Capacity to Transplant Many Grafts in a Single Session: FUT is perfect for individuals with significant hair loss because it enables the transplantation of multiple grafts in a single session.
- Potentially Lower Cost: FUT is generally less expensive than FUE because it involves a more straightforward extraction process and can be completed in a shorter timeframe.
Disadvantages
- Linear Scarring: Removing a scalp strip results in a linear scar at the donor site. While surrounding hair can conceal this scar, it may be visible if worn very short.
- Longer Recovery Time: Due to the strip removal and suturing nature, recovery from FUT can be extended. Patients may experience more discomfort and need longer to heal than FUE.
Despite these drawbacks, FUT remains a valuable option for those requiring a substantial number of grafts in a single session and looking for a more cost-effective solution to hair transplantation.
FUE and FUT Hair Transplant Cost Comparison
Cost is a significant factor when considering a hair transplant. FUE and FUT have different pricing structures based on the method, complexity, and number of grafts required. Here’s a simplified comparison to help you understand the cost differences.
- Number of Grafts: More grafts increase the cost.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: Highly experienced surgeons charge more.
- Location: Costs vary by geographical area and clinic reputation.
- Procedure Complexity: More intricate procedures can be pricier.
Cost Comparison Table in INR
| Graft Needs | FUE Cost per Graft | FUE Total Cost Range | FUT Cost per Graft | FUT Total Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (up to 1000 grafts) | INR RS10 – RS120 | INR RS10,000 – RS1,20,000 | INR RS30 – RS70 | INR RS30,000 – RS70,000 |
| Medium (1001 – 2000 grafts) | INR RS10 – RS120 | INR RS20,000 – RS2,40,000 | INR RS30 – RS70 | INR RS60,000 – RS1,40,000 |
| High (more than 2000 grafts) | INR RS10 – 1RS20 | INR RS30,000 – RS3,60,000 | INR RS30 – RS70 | INR RS90,000 – RS2,10,000 |
Cost Comparison Table in USD
| Aspect | FUE | FUT |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per Graft | $5 – $15 | $3 – $10 |
| Total Procedure Cost | $4,000 – $15,000 | $3,000 – $10,000 |
| Scarring | Minimal (pinpoint scars) | More noticeable (linear scar) |
| Recovery Time | Faster (few days) | Longer (several weeks) |
Remember, these are average ranges, and the exact cost can vary based on the clinic, location, and the extent of the transplant needed. It’s always best to consult a FUE and FUT hair transplant specialist to get a precise estimate for your situation.
Who is eligible for a FUE and FUT hair transplant

Eligibility for a FUE and FUT hair transplant is determined by several factors that ensure the procedure is safe and likely to be successful. Here are the general criteria for someone considering a hair transplant:
For young patients, particularly those under 21, the decision is more challenging because it is difficult to foresee how hair loss will continue, and there is a risk of unrealistic expectations about the outcome.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified hair transplant surgeon who can evaluate your specific situation and determine if you meet these criteria. They will consider your hair loss pattern, donor hair quantity and quality, and overall health to decide if a FUE and FUT hair transplant suits you.
Give up smoking and alcohol. Both may prevent hair follicles from growing and repairing. Keep befor and after away from the FUE and FUT hair transplants for at least a month afterward.
Critical Differences Between FUE and FUT: A Step-by-Step How-To Guide
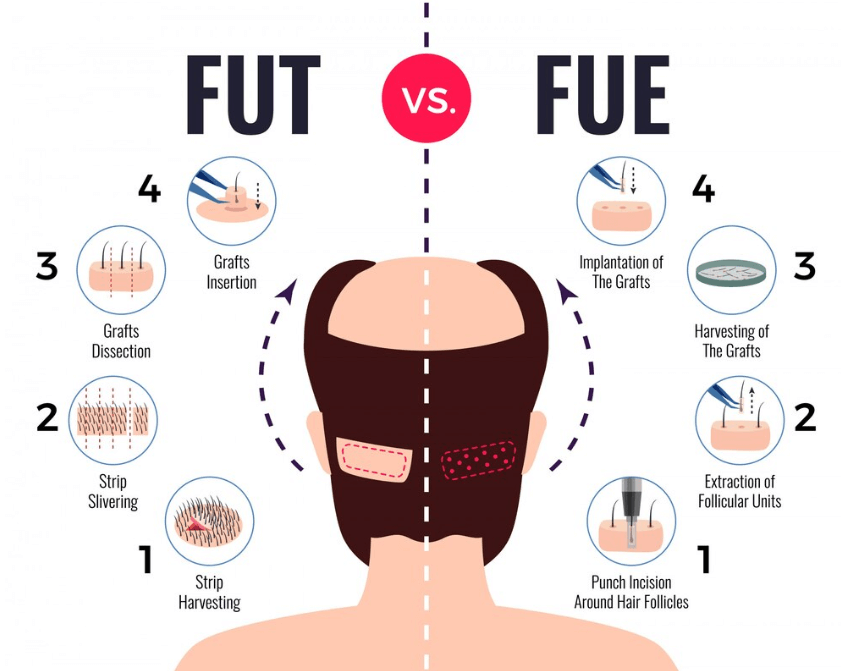
Understanding the critical differences between FUE and FUT(Follicular Unit Extraction and Follicular Unit Transplantation) is essential for choosing the proper hair transplant method for your needs. This directory will walk you through the steps to compare these two techniques effectively.
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
Individual Follicles: Hair follicles are extracted one by one from the donor area using a micro-punch tool.
Precision: This method allows for precise extraction, minimizing damage to surrounding follicles.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)
Strip of Scalp: A strip of scalp is surgically removed from the donor area.
Dissection: The strip is then divided into individual follicular units under a microscope.
FUE Scarring
Pinpoint Scars: Tiny, circular scars are left at each extraction site.
Less Noticeable: These scars are typically less noticeable and heal quickly.
FUT Scarring
Linear Scar: A single linear scar is left where the strip was removed.
Visibility: The scar can be concealed by surrounding hair but may be visible if the hair is worn very short.
FUE Recovery Time
Quick Healing: Due to the minimally invasive nature, FUE has a faster recovery time.
Return to Activities: Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days.
FUT Recovery Time
More extended Healing Period: The larger surgical area means a longer recovery.
Activity Restrictions: Patients may need to avoid strenuous activities for longer.
FUE Cost
Higher Per Graft: FUE generally costs more per graft due to the individual extraction process.
Overall Cost: The total cost can range significantly based on the number of grafts needed and the surgeon’s expertise.
FUT Cost
Lower Per Graft: FUT typically costs less per graft due to the strip method.
Overall Cost: This method can be more cost-effective for large areas of hair loss.
FUE Suitability
Hair Type: Suitable for those with tighter scalp skin or finer hair.
Extent of Hair Loss: Ideal for patients needing fewer grafts or those seeking minimal scarring.
Personal Preferences: Preferred by those who want a quicker recovery and less noticeable scarring.
FUT Suitability
Hair Type: Suitable for those with looser scalp skin and thicker hair.
Extent of Hair Loss: Ideal for patients needing many grafts in a single session.
Personal Preferences: Preferred by those prioritizing cost-effectiveness and tolerating a more extended recovery period.
following a FUE and FUT hair transplant Continue using any topical treatments that might promote healing in addition to any prescription medications, like antibiotics, to prevent infections.
How to Choose Between FUE and FUT Hair Transplant
Choosing between FUE and FUT requires careful consideration of various factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you decide which method is suitable for you:
FUE: Suitable for individuals with tighter scalp skin or finer hair.
Works well for those with adequate donor hair density.
FUT: Appropriate for individuals with looser scalp skin and thicker hair.
It can be advantageous for those with high hair density as it allows for transplanting many grafts.
FUE: It is ideal for smaller balding areas or when a limited number of grafts are needed.
Effective for filling in specific areas of thinning hair or receding hairlines.
FUT: It is beneficial for larger balding areas or when many grafts are required.
Suitable for covering extensive hair loss in a single session.
FUE: They are preferred by individuals who prioritize minimal scarring and quicker recovery.
Suitable for those with active lifestyles who want to resume normal activities sooner.
FUT: She was chosen by individuals who prioritize cost-effectiveness and are willing to tolerate a more extended recovery period.
It is preferable for those with a less active lifestyle who can accommodate a more extended downtime.
Make an appointment for a consultation with a licensed hair transplant expert.
Discuss your goals, dreams, and concerns around hair loss.
Let the specialist assess the kind, density, and pattern of your hair balding.
Receive recommendations that are tailored to your likes and needs.
Review real-life examples or case studies of individuals who have undergone FUE and FUT procedures if available.
Consider their experiences, results, and satisfaction levels.
Use these insights to inform your decision-making process further.
Choosing between FUE and FUT requires careful consideration of factors such as hair type, balding area size, personal preferences, and lifestyle. Speaking with a hair transplant specialist to get customized guidance and suggestions is essential. By considering these aspects and getting expert advice, you can select wisely based on your expectations and aspirations.
Discuss with your surgeon the safe return date for regular hair styling. Handle your hair gently to avoid damaging the new hair grafts.
Conclusion
A crucial first step in treating hair loss is choosing between FUE and FUT,(follicular unit extraction and follicular unit transplantation). When considering your alternatives, it’s necessary to comprehend the important distinctions between these two approaches so that you can make the best decision for your situation.
Your decision between FUE and FUT may significantly impact your hair restoration journey. You can ensure that you select the method that best suits your objectives and way of life by being aware of the variations and accounting for factors like hair type, the size of the balding area, and personal preferences.
The most important thing to do when deciding is to consult with a hair transplant professional. These specialists possess the knowledge and experience to evaluate your circumstances, make tailored recommendations, and direct you toward the best course of action. A consultation will provide the clarity and assurance you need to proceed with your hair restoration journey, regardless of your preference for FUE and FUT.
Recall that you are not travelling alone. With the help of experienced pros, you can take the first step toward getting the hair transformation you’ve always wanted and recovering your confidence. Make an appointment right now to start on the road to a more vivid, fuller head of hair.
FAQs: About FUE and FUT
Which procedure hurts more, FUE or FUT?
There is minimal discomfort with FUE and FUT operations because they are done under local anaesthesia. However, depending on their pain threshold and the complexity of the surgery, some patients may have slight discomfort or soreness in the following days.
How long do the results of FUE and FUT last?
The results of both FUE and FUT hair transplants are typically permanent. Once the transplanted hair follicles take root in the recipient area, they grow naturally, like regular hair. However, following post-operative care instructions and maintaining overall scalp health is essential to optimize long-term results.
Can FUE and FUT methods be combined for a single procedure?
Yes, FUE and FUT methods can be combined in a single procedure, depending on the patient’s specific needs and the surgeon’s recommendation. This hybrid approach, known as a combination or hybrid hair transplant, allows for the advantages of both methods to be utilized, maximizing graft yield and minimizing scarring.
What factors determine the success of a FUE or FUT hair transplant?
Several factors contribute to the success of an FUE and FUT hair transplant, including the surgeon’s skill and experience, the quality of the donor’s hair, the density and elasticity of the scalp, and adherence to post-operative care instructions. Factors like overall health, lifestyle habits, and genetics can influence the outcome.
Are FUE and FUT appropriate for both genders?
Yes, hair loss sufferers of both sexes can benefit from FUE and FUT hair transplant techniques. However, specific characteristics, including hair type, scalp health, and degree of hair loss, may affect a person’s eligibility for each therapy. A professional consultation with a hair transplant professional can offer tailored advice based on these variables.
Which hair transplant is the most successful?
With 90% graft survival rates, FUE transplants can be as effective as the more established FUT procedure. Using robotic FUE technology, the treatment success rate can reach 100%. The level of success depends on the skill, experience, and training of the doctor administering the care.

