Although hair loss in women is one of the most common issues, it is often considered unimportant or ignored in the discussion of health and beauty. Contrary to a general belief, hair loss is a global issue encountered by millions of women and has a detrimental effect on their self-esteem, confidence, and overall quality of life.
Hair loss in women and Hair loss in men can be a stressful illness that causes changes in their lives as well as affects their psychological traits.
Understanding the causes of hair loss is a crucial step towards managing and overcoming this issue. By focusing on baldness, a sensitive yet common issue in women, we aim to empower our audience with knowledge. We delve into the main factors behind Female Pattern Baldness, such as hormonal shifts and inherited characteristics, to provide a comprehensive understanding.
We plan to offer valuable solutions that empower women to take charge of their hair condition. We discuss medical treatments, management approaches, and other potential solutions. By emphasizing the practicality of these solutions, we aim to instil hope and reassurance in our audience, assuring them that healthy hair regrowth and regained confidence are within reach.
A new season with us will be dedicated to the causes of hair loss in women and practical solutions to grow thick, beautiful hair and confidence.
Learn how stress management practices can increase the effectiveness of women’s hair loss treatments.
Understanding Hair Loss in Women
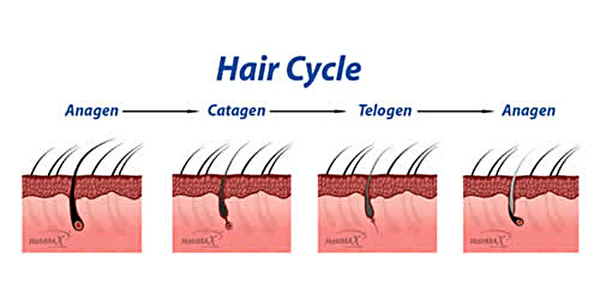
The growth cycle, a cyclical pattern, controls the dynamic hair growth process. Comprehending this cycle is essential to understanding the mechanics underlying female hair loss.
There are three primary phases to the hair growth cycle:
- Anagen Phase: The active growth or anagen phase is when hair follicles generate new strands. Depending on the individual, the anagen period may last two to seven years.
- Catagen Phase: In this transitional phase, hair growth slows, and the hair follicle shrinks. It typically lasts for a few weeks.
- Telogen Phase: The resting phase involves Hair follicles remaining inactive and shedding old Hair to make way for new ones. It lasts for approximately three months before the cycle repeats.
When this natural cycle is disturbed, hair loss may result. Women experience hair loss mostly in two ways:
Statistics on the frequency of hair loss among women underscore the significance of this issue. According to research, approximately 40% of women experience visible hair loss by age 40, with the prevalence increasing. Despite its prevalence, hair loss in women is often stigmatized and overlooked, highlighting the need for greater awareness and understanding of this condition.
In the following sections, we’ll examine why women experience hair loss and discuss doable preventative and treatment options.
Causes of Hair Loss in Women

Numerous causes, including hormone imbalances, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle effects, might contribute to hair loss in women. To adequately address and manage hair loss, it is imperative to comprehend these underlying causes. The following are some typical causes of hair loss in women:
1. Hormonal Factors:
2. Genetic Predisposition:
3. Nutritional Deficiencies:
4. Stress and Its Impact on Hair Health:
5. Medical Conditions and Medications:
Addressing these underlying causes through targeted interventions and lifestyle modifications can often improve hair health and regrowth in women experiencing hair loss. The following sections will explore potential treatment options and holistic approaches for managing hair loss effectively.
See a dermatologist or hair specialist if you experience noticeable hair loss so that you can determine the underlying cause and obtain the necessary therapy. Prompt action can aid in halting additional hair loss.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
A healthcare expert should thoroughly evaluate and diagnose hair loss as a complex and multifaceted disease. An experienced healthcare provider should be consulted for an accurate diagnosis and customized treatment planning. This is why it’s so important to get competent advice:
- Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional:
- Common Diagnostic Methods:
- Understanding the Significance of Identifying the Underlying Cause:
Through a comprehensive assessment and diagnosis by a medical practitioner, people suffering from hair loss can learn important information about their condition and receive the assistance and treatment they need. In the following parts, we will look at different approaches to treatment and effective hair loss management.
Treatment Options

Surgical techniques, oral drugs, nutritional interventions, topical therapies, and lifestyle alterations are some methods used to treat female hair loss. Women experiencing hair loss may consider the following standard treatments:
1. Topical Treatments:
2. Oral Medications:
3. Nutritional Supplements and Dietary Changes:
4. Hair Transplant Surgery:
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
A healthcare professional’s advice is crucial in deciding on the best course for treating hair loss, considering each patient’s unique needs, medical history, and underlying reasons. Achieving the best possible outcomes requires sticking to treatment plans and having reasonable expectations.
Smoking and binge drinking have been shown to have detrimental effects on hair health. Reducing alcohol consumption and giving up smoking can enhance general health and hair condition.
Natural Remedies and Home Care
In addition to medical treatments and interventions, natural remedies and home care practices can play a supportive role in promoting hair growth and maintaining overall hair health. The following natural therapies and hair-growth-optimizing home care advice will help you manage hair loss:
1. Herbal Remedies and Essential Oils:
2. Tips for Maintaining Healthy Hair at Home:
Incorporating natural remedies and at-home hair care techniques into your regimen can improve the general state of your hair, minimize damage, and encourage healthy hair growth. Consistency and patience are essential to getting the desired results, as with any hair care routine.
Choose sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners designed for your hair type. Avoid products containing harsh chemicals that might deplete your hair’s natural oils and cause damage.
Conclusion
Hair loss in women is a complex problem with broad emotional, psychological, and practical ramifications. We have covered a variety of treatment approaches and coping mechanisms in addition to exploring the many reasons for hair loss, which range from hormonal variables to hereditary predispositions.
It’s important to remember the key points discussed:
Hair loss in women is a prevalent worry that can affect one’s sense of self-worth, perception of one’s body, and general well-being.
Comprehending the reasons behind hair loss is imperative for efficient therapy and administration.
Topical therapies, oral drugs, dietary changes, surgery, and lifestyle adjustments are among the available forms of treatment.
Seeking emotional and practical assistance from family members and medical professionals is essential.
Coping strategies, including acceptance, self-affirmations, stress management, and support networks, can help women courageously face the difficulties of hair loss.
We stress the significance of accepting self-care and keeping an optimistic mindset when dealing with hair loss. Remember to cherish your inner beauty and power and to give priority to your physical and emotional well-being. By taking care of yourself with self-love, acceptance, and resilience, you may overcome the difficulties associated with hair loss and gracefully and confidently appreciate your individual beauty.
FAQs about Hair Loss in Women
What makes ladies lose their hair?
Several causes, including hormonal shifts (such as menopause or thyroid issues), genetic predispositions (such as female pattern hair loss), dietary deficiencies, stress, illnesses, and some drugs, can cause hair loss in women.
Is female hair loss average?
Indeed, millions of women worldwide suffer from hair loss. Though it’s frequently discussed more about men, hair loss in women is a severe problem that can affect one’s quality of life and sense of self.
How is hair loss in women diagnosed?
A complete medical history, a physical examination, and occasionally additional blood tests or scalp biopsies to discover underlying causes are all part of the diagnosis process.
How do women deal with the psychological effects of hair loss?
To manage the psychological effects of hair loss, one can practice self-care and self-acceptance, seek assistance from loved ones and medical professionals, and consider coping strategies such as counselling, support groups, and stress management methods.
Is it possible to prevent hair loss in women?
Appropriate hair care practices, treating underlying medical issues, and leading a healthy lifestyle can all help reduce hair loss and enhance ideal hair health, even if some reasons for hair loss may not be preventable.
Does hair loss in women differ from hair loss in men?
Men and women can both experience hair loss, but the underlying causes and patterns are frequently different. The classic signs of male pattern baldness are thinning at the crown and a receding hairline. On the other hand, total hair thinning, particularly on the top of the scalp, is typically the result of female pattern hair loss.
Are any aspects of a woman’s lifestyle contributing to her hair loss?
Women who experience hair loss may be affected by confident lifestyle choices, including smoking, high levels of stress, crash dieting, tight hairstyles that tug on the hair strands (such as tight ponytails or braids), and excessive heat styling.
Are there any age-related factors associated with hair loss in women?
Yes, age can play a role in hair loss in women, as hormonal changes associated with menopause and ageing can affect hair growth and thickness. Additionally, as women age, the hair growth cycle may slow down, leading to gradual thinning over time.

