Do you ever worry because your are losing hair? In this extensive tutorial, we’ll examine two common approaches to hair restoration: hair replacement and hair transplantation.
Are you tired of having bald spots or weak hair? Drawing a differentiation between the two is a part of it. You will have the chance to determine if you are seeking a more temporary or permanent solution after hearing about the intricacies of each approach.
This is the best information on techniques for growing thick hair. You will be given a comprehensive understanding of the differences between Hair Transplant vs. hair restoration, as well as motivation and hope to take the initial step toward accepting hair growth and rebuilding your self-worth.
This strategy highlights how Hair Restoration technology is developing, with FUE and FUT serving as key players.
Hair Transplantation
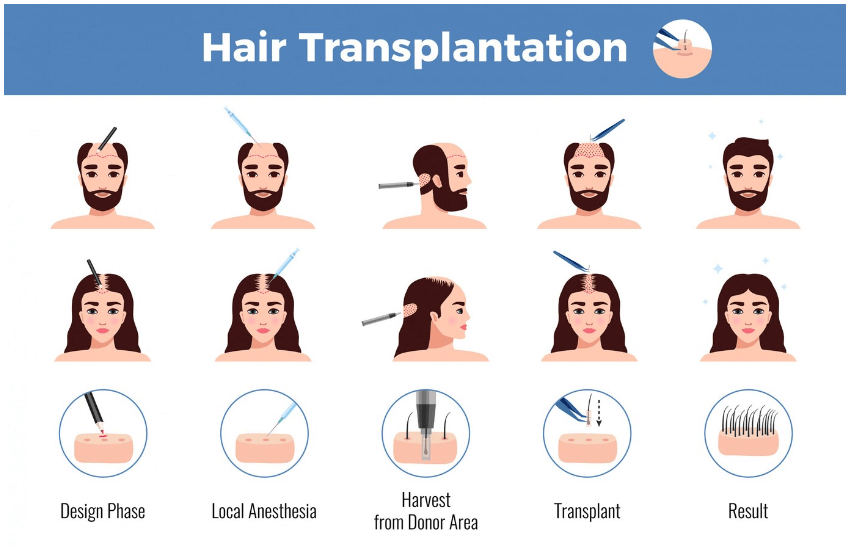
Hair restoration in thinning hair or hair-losing areas of the scalp is accomplished surgically through hair transplantation. It entails the transplantation of hair follicles, usually through Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), from a donor site to the recipient site.
Procedure Explanation:
Pros of Hair Transplantation:
| Permanent Results: | Transplanted hair continues to grow naturally for a lifetime. |
| Natural Appearance: | Results look and feel natural, blending seamlessly with existing hair. |
| Minimal Maintenance: | Once transplanted, the hair requires no special care or Maintenance. |
| Increased Confidence: | Converting a fuller head of hair can boost self-esteem and confidence levels. |
Cons of Hair Transplantation:
| Surgical Procedure: | Like any surgery, hair transplantation carries risks such as infection, bleeding, or scarring. |
| Cost: | Hair transplant methods can be expensive, particularly for more comprehensive treatment areas. |
| Recovery Time: | Patients may experience temporary swelling, discomfort, or numbness post-surgery |
| Limited Donor Hair: | The procedure’s success depends on an adequate donor hair supply. |
Comprehending the intricacies of hair transplantation can help individuals make knowledgeable decisions about handling their hair loss concerns and achieving desired results.
Non-surgical methods may necessitate repeated use to maintain outcomes. Discontinuing treatment may negate the benefits, however hair transplantation provides lasting effects once the transplanted hair follicles have taken root.
Hair Restoration:
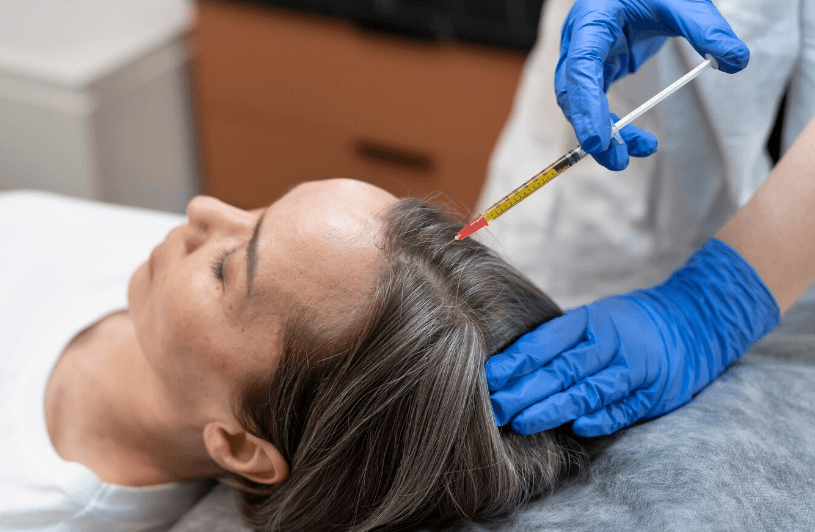
Hair restoration refers to restoring or regrowing hair in areas of hair loss or thinning. It involves addressing the underlying causes of hair loss and promoting new hair growth to achieve a fuller appearance.
Different Approaches to Hair Restoration:
- 1. Medical Treatments:
Prescription Medications: Oral medicines like finasteride (Propecia) and topical explanations like minoxidil (Rogaine) are typically used to slow down hair loss and promote regrowth.
Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients essential for hair health may be recommended to support hair growth.
- 2.Non-Surgical Procedures:
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP involves pulling a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to separate platelet-rich plasma, and injecting it into the scalp to promote hair follicle growth.
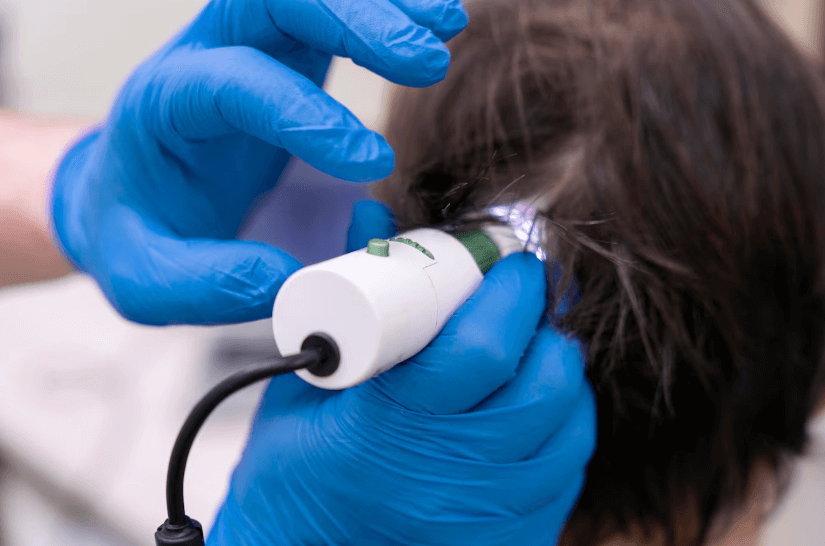
Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices emit red light to stimulate hair follicles, improve circulation, and promote growth.
Pros of Hair Restoration:
| Non-Invasive: | Many hair restoration methods are non-surgical, minimizing downtime and recovery. |
| Versatile Options: | From medications to non-surgical techniques, individuals have a range of therapy options to select from. |
| Improved Hair Health: | Some treatments promote hair growth and improve living hair’s general health and grade. |
| Convenience: | Non-surgical procedures like PRP therapy can typically be performed in the office with minimal disruption to daily activities. |
Cons of Hair Restoration:
| Variable Results: | The effectiveness of hair restoration treatments can vary from person to person, and results may not be guaranteed. |
| Ongoing Maintenance: | Some treatments require ongoing use or Maintenance to sustain results, which can incur additional costs. |
| Limited Coverage: | Hair restoration treatments may not be suitable for advanced or extensive hair loss cases. |
| Cost Considerations: | While non-surgical procedures may be more affordable upfront, long-term costs can add up. |
Understanding the different approaches to hair restoration and considering the pros and cons can help someone choose the most suitable option for addressing their hair loss concerns and achieving the desired results.
Advantages and Disadvantages Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration

Hair Transplant
Advantages
- Permanent Solution: Hair transplantation offers a long-term explanation for hair loss. The transplanted hair restarts to grow naturally for a lifetime, providing lasting results and eliminating the need for ongoing treatments.
- Natural-Looking Results: Transplanted hair blends seamlessly with existing hair, resulting in a natural appearance. This enhances the overall aesthetic and boosts self-confidence, as the hairline and density appear authentic.
- Minimal Maintenance: Minimal Maintenance is required once the transplanted hair has fully grown. Routine hair care practices, such as washing and styling, are sufficient to maintain the natural look and feel of the hair.
Disadvantages
- Surgical Procedure with Associated Risks: Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves risks such as infection, bleeding, and scarring. While these risks are typically low, they should be considered when undergoing the procedure.
- Longer Recovery Time: Patients may experience a more prolonged recovery following hair transplantation than non-surgical alternatives. This includes temporary swelling, discomfort, and numbness in the scalp, which can persist for several days to weeks post-surgery.
- Higher Initial Cost Compared to Some Alternatives: Hair transplantation can be more costly upfront than non-surgical treatments. Although the initial investment may be higher, the procedure offers permanent results, eliminating the need for ongoing expenses associated with other treatments.
Hair Restoration
Advantages
- Permanent Solution: Hair restoration methods offer a long-lasting solution to hair loss, providing results that can endure over time. This permanence eliminates the need for frequent Maintenance or repeat treatments.
- Natural-Looking Results: Restored hair appears natural and blends seamlessly with existing hair, creating a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing appearance. This natural look enhances self-confidence and makes individuals feel comfortable in their skin.
- Minimal Maintenance Required: Once hair restoration is complete, minimal Maintenance is needed to preserve the results. Routine hair care practices, such as washing and styling, are typically sufficient to maintain the restored hair’s appearance and health.
Disadvantages
- Surgical Procedure with Associated Risks: Some hair restoration methods involve surgical procedures that carry inherent risks, including infection, bleeding, and scarring. While these risks are generally low, they should be considered when undergoing treatment.
- Longer Recovery Time: Patients may experience a more extended recovery following hair restoration surgery than non-surgical alternatives. This can include temporary discomfort, swelling, and limitations on physical activity during the healing process.
- Higher Initial Cost Compared to Some Alternatives: Hair restoration procedures can be more costly upfront than non-surgical treatments. Although the initial investment for surgery may be higher, the permanent results justify the higher initial cost over time.
Thinking in getting a full head of hair back through hair restoration? It is important to compare the benefits and drawbacks with your goals and budget. This will assist you in determining if hair restoration—including alternatives such as hair transplant vs. hair restoration—is the best course of action for you.
Suitability: Non-surgical treatments may be a preferable alternative for those with limited donor hair or experiencing early hair loss. More severe cases of hair loss are often reserved for surgical procedures.
Factors to Consider Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration
Cost Comparison:Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration
| Hair Restoration Method | Hair Transplant | Hair Restoration (Non-surgical) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Cost | ~ INR 60,000 to INR 400,000 /INR 30,000 to INR 5,00,000, | ~ INR 20,000 to INR 60,000 [2-6 sessions] |
| Advantages | Permanent results – Natural appearance | Lower initial cost – Non-invasive |
| Disadvantages | Higher initial cost – Surgical procedure with associated risks | Results may vary – Ongoing maintenance required |
Timeframe for Results: Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration
| Hair Restoration Method | Hair Transplant | Hair Restoration (Non-surgical) |
|---|---|---|
| Timeframe for Results | 6 to 12 months | Few months |
| Advantages | Permanent results – Natural appearance | Faster results – Minimal downtime |
| Disadvantages | Longer recovery time – Full results may take time | Results may vary – Maintenance required for sustained results |
Suitability for Different Types of Hair Loss: Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration
| Hair Restoration Method | Hair Transplant | Hair Restoration (Non-surgical) |
|---|---|---|
| Suitability | Advanced hair loss | Early to moderate hair loss |
| Advantages | Permanent solution – Suitable for extensive balding | Non-invasive – Lower cost |
| Disadvantages | Limited donor hair – Surgical procedure risks | Limited efficacy for advanced hair loss – Results may not be permanent |
Other Factors to Consider Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration
| Other Factors | Hair Transplant | Hair Restoration (Non-surgical) |
|---|---|---|
| Long-Term Maintenance | Minimal Maintenance is required after recovery. | Ongoing Maintenance may be necessary for sustained results. |
| Risk and Recovery | Surgical procedure with associated risks such as infection and scarring. | Non-invasive procedures with minimal risks and shorter recovery periods. |
| Individual Preferences | Ideal for individuals seeking permanent and natural-looking results. | Suitable for those preferring non-invasive options with lower upfront costs. |
| Consultation and Expert Advice | Consultation with a qualified surgeon is essential for evaluation and planning. | Consult a specialist to determine the most suitable treatment approach and address concerns. |
Non-surgical options provide alternatives to surgical procedures for individuals seeking to combat hair loss. These methods include medications, supplements, and topical treatments, each offering varying effectiveness and convenience.
Overview of Non-Surgical Options:
Conclusion
We’ve looked at the available choices for treating hair loss, concentrating on hair restoration techniques that don’t require surgery. Below is a summary of the main ideas covered:
We compared the advantages and disadvantages of surgical procedures like hair transplantation with non-surgical options such as medications, supplements, and topical treatments.
Both surgical and non-surgical methods offer unique benefits and limitations. While surgical procedures provide permanent results and natural-looking hair, they have associated risks and higher initial costs. Non-surgical options may offer convenience and lower upfront expenses but require ongoing Maintenance for sustained results.
If you’re experiencing hair loss, taking proactive steps to address it is essential. Whether you choose a surgical or non-surgical procedure, proper treatments are available to help restore your confidence and regain a full head of hair.
Make the most of your life; don’t let hair loss stop you. There’s no need to suffer in silence thanks to developments in hair restoration technology and various treatment alternatives. Make an appointment for a consultation with a licensed hair restoration specialist right now to regain your confidence. Now is the time to begin your road to a more vivid, fuller head of hair.
FAQs for Hair Transplant vs. Hair Restoration
What distinguishes a from a hair transplant vs. hair restoration?
Hair transplant: involves surgically transplanting hair follicles from donor areas to balding or thinning areas.
Hair restoration encompasses various methods, including surgical and non-surgical options, to promote hair growth and improve the appearance of thinning or receding hairlines.Are the consequences of a hair transplant permanent?
Since transplanted hair follicles continue to grow naturally in their new site, hair transplant results are usually permanent. However, more hair loss in the surrounding areas can happen over time, necessitating maintenance treatments to maintain the effects.
How long does it take to see results from a hair transplant vs. hair restoration procedure?
Results vary depending on the method chosen and individual factors. With hair transplant surgery, visible results typically appear within 6 to 12 months, while non-surgical treatments may show results within a few months of initiation.
Are there any risks involved with hair transplant vs. hair restoration techniques?
Both hair transplant vs. hair restoration procedures carry risks such as infection, bleeding, scarring, and allergic reactions to medications or anesthesia. Discussing potential dangers with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing treatment is essential.
How long does it take to recover from hair transplant vs. hair restoration?
Recovery timeframes differ based on the treatment and the patient’s recovery rate. Following hair transplant surgery, patients may have short-term swelling, scabbing, and soreness. Recovery usually takes a few days to a few weeks.
What is the cost of hair transplant vs. hair restoration?
The method selected, the length of treatment needed, and the clinic’s location are some variables that impact the cost of a hair transplant vs. hair restoration. The initial cost of surgical treatments, such as hair transplantation, is higher than non-surgical ones.
Are hair transplant vs. hair restoration procedures available to women?
Both men and women can get hair transplant vs. hair restoration or to combat hair loss. To ascertain the best course of action for treating hair loss, it is imperative to speak with an expert, as the causes and patterns of hair loss may vary between genders.

