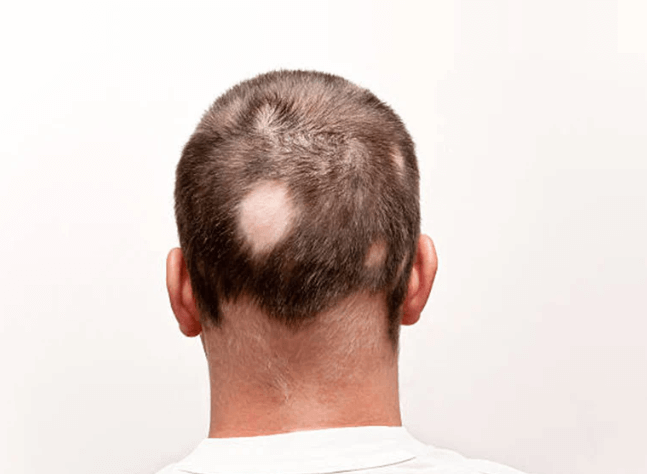
Alopecia, popularly referred to as hair loss, is a global problem affecting millions of people. It includes a variety of illnesses that cause the scalp or other body areas to lose all or part of their hair. Alopecia can take many forms, such as telogen effluvium, alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia. Still, it can significantly affect one’s quality of life and sense of self.
Topical treatments for alopecia play a pivotal role in hair loss management. These treatments, applied directly to the scalp or affected areas, offer a noninvasive and convenient approach to stimulating hair growth and slowing down hair loss progression. From over-the-counter solutions to prescription medications, the world of topical treatments for alopecia is diverse and continually evolving.
We will discuss topical treatments for alopecia and the variety of options available to those seeking to manage their hair loss. By investigating the workings, efficacy, and possible adverse effects of popular topical treatments, we intend to arm our readers with the knowledge they need to make wise judgments regarding the health of their hair.
What is Alopecia?
Definition and Rationale Alopecia areata is an autoimmune illness that causes patchy hair loss. It is brought on by the immune system mistakenly targeting the hair follicles. It can appear anywhere on the body, but the scalp is the most common place to observe it.
There are three main severity degrees of the condition: alopecia areata, which causes small, coin-sized patches of hair loss; alopecia to this, which causes whole scalp hair loss; and alopecia universalis, which causes total body hair loss.
Alopecia is a complex disorder that causes hair loss on the scalp or in other body parts, entirely or partially. It can take many forms and is frequently categorized according to the causes and patterns of hair loss. Comprehending the subtleties of alopecia is essential for proficient handling and assistance for those impacted by this disorder.
Common Types of Alopecia:
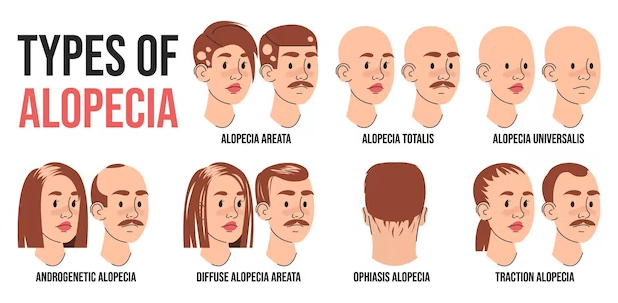
- Androgenetic Alopecia: The most general type of hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, also called male or female pattern baldness. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and genetic predisposition are thought to have an impact. Usually, this alopecia causes a slow thinning of hair over time, beginning at the crown or temples and moving to other parts of the scalp.
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune infection is characterized by brief, erratic hair loss, resulting from the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles locally. Rarely alopecia areata can progress to universalis, alopecia totalis, or total loss of body hair. Universalis is the complete loss of scalp hair.
- Telogen Effluvium: A transient type of hair loss brought on by interferences with the hair growth cycle is called telogen effluvium. Sickness, stress, hormonal fluctuations, or specific drugs can bring it on. Usually, telogen effluvium causes diffuse hair loss throughout the scalp instead of isolated bald spots.
Benefits of Topical Treatments for Alopecia
Let’s examine some of the main advantages of applying topical treatments for alopecia :
By harnessing the benefits of topical treatments for alopecia, individuals can take proactive steps to address their hair loss concerns and regain confidence in their appearance. With their noninvasive nature, convenience, and targeted action, topical treatments offer a promising avenue for promoting hair growth and achieving lasting improvements in health and vitality.
Common Topical Treatments for Alopecia

Alopecia can be managed with various topical therapies, each with unique efficaciousness and mechanisms of action. Among the topical Treatments for Alopecia that are most frequently utilized are:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Minoxidil is used topically on the scalp as a foam or solution. It functions by lengthening the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle, widening blood vessels in the scalp, and enhancing blood flow to hair follicles. Minoxidil is available over-the-counter and is approved by the FDA to treat androgenetic alopecia or male and female pattern baldness.
- Finasteride (Propecia): Finasteride is mainly taken orally; however, certain compounding pharmacies also provide topical versions. Finasteride prevents the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to the shrinkage of hair follicles, by blocking the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Topical finasteride may provide a targeted method of lowering scalp DHT levels, slowing hair loss and encouraging growth.
- Corticosteroids: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that causes patchy hair loss. Topical corticosteroids are frequently used to treat this illness. To promote hair regrowth, corticosteroids suppress the immune system and lessen inflammation in the scalp’s afflicted areas. Several formulations of these drugs are available, including creams, lotions, and ointments.
- Anthralin (Dithranol): This topical drug treats alopecia areata and other forms of hair loss. It modifies the skin’s immunological response and encourages new hair growth. Usually, anthralin is applied to the scalp’s afflicted regions and kept on briefly before being cleaned off.
- Topical Immunotherapy: This treatment involves applying a sensitizing agent, such as diphencyprone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutyl ester (SADBE), to the scalp to induce an allergic reaction. The immune response generated by the sensitizing agent can stimulate hair regrowth in individuals with alopecia areata.
- Essential Oils and Herbal Extracts: Some individuals may opt for natural remedies, such as essential oils (e.g., rosemary oil, peppermint oil) and herbal extracts (e.g., saw Palmetto), to promote hair growth and improve scalp health. While research on the efficacy of these treatments is limited, some people find them beneficial as adjunctive therapies.
Carefully read and adhere to the directions that came with your topical therapy. Take note of the dosage, the frequency of administration, and any additional usage instructions.
Natural and Herbal Remedies for Alopecia:
Essential Oils:
Rosemary Oil:
Peppermint Oil:
Herbal Extracts:
Saw Palmetto:
Potential Benefits of Natural Remedies:
Limitations of Natural Remedies:
Combination Approach:
Caution and Consultation:
Natural and herbal remedies can offer a gentle and accessible approach to promoting hair growth and scalp health. While they may not be as extensively studied or rapidly effective as conventional treatments for Alopecia, they can complement existing regimens and provide individuals with additional options for managing alopecia.
Make sure your scalp is clean and clear of debris, oil, and styling products before using topical treatments.
New and Emerging Topical Treatments for Alopecia:
- Nanotechnology-Based Formulations:
- Stem Cell-Based Therapies:
- Peptide-Based Treatments:
- Botanical Extracts and Phytochemicals:
- Microbiome-Based Therapies:
These advancements in topical treatments for alopecia represent exciting avenues of research and development, offering hope for improved outcomes and treatment options for individuals with hair loss conditions. Continued investment in innovative therapies and clinical research is essential to bring these promising treatments to fruition and address the diverse needs of individuals affected by alopecia.
The management of alopecia requires time and patience. Remain optimistic and committed to your treatment plan despite your modest improvement.
Consultation and Professional Guidance Before Starting Topical Treatments for Alopecia

Conclusion
Managing alopecia involves a variety of topical Treatments for Alopecia, each with its advantages and drawbacks. People have various options, from traditional solutions like minoxidil and corticosteroids to cutting-edge treatments, including formulations based on nanotechnology and natural cures. Still, seeking individualized advice from healthcare specialists is crucial.
People seeking professional guidance customized to their needs can manage their hair loss journey confidently and effectively. Regaining control over one’s health and managing hair loss concerns require proactive measures and well-informed decision-making.
By seeking professional guidance and taking proactive steps towards managing their hair loss, individuals can empower themselves to regain confidence in their appearance and embrace their hair health journey with resilience and optimism.
Implementing these useful suggestions into your hair care regimen can optimize the efficacy of topical treatments for Alopecia and promote healthy hair development.
FAQs for Topical Treatments for Alopecia
-
What is alopecia, and what causes it?
Alopecia is the term for hair loss that results from an immune system attack on hair follicles. Genetics, autoimmune diseases, including alopecia areata, hormonal fluctuations, pharmacological interventions, and stress are some of the causes.
-
What are topical treatments for alopecia, and how do they work?
Topical treatments for alopecia involves medications or formulations applied directly to the scalp to promote hair growth or lessen hair loss. Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, corticosteroids reduce inflammation, and finasteride inhibits the DHT hormone.
-
Are topical treatments for alopecia effective for all types of alopecia?
Specific alopecia, such as mild to moderate occurrences of alopecia areata or androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness), may respond better to topical therapies. However, its efficacy may differ based on the person and the particular kind of hair loss.
-
How long does it take to see results from topical treatments for alopecia?
The timeline for seeing results from topical treatments can vary, with some individuals noticing improvements in hair growth or reduction in hair loss within a few months, while others may take longer. Consistent use as directed is essential for optimal results.
-
What are the potential side effects of topical treatments for alopecia?
While generally considered safe, topical treatments for alopecia may be associated with side effects such as scalp irritation, itching, or dryness. These side effects are usually mild and temporary but should be monitored, and a healthcare professional should be consulted if they persist or worsen.
-
Can topical treatments be used in combination with other treatments for alopecia?
Yes, topical treatments for alopecia can frequently be used in conjunction with injections, oral drugs, and laser therapy. Combining therapies can increase their effectiveness, but speaking with a healthcare provider is essential to guarantee safety and compatibility.

